Quality use of WRONG ROUTE ADMINISTRATION OF ORAL staff on the progress towards improving and maintaining systems for safe oral route administration. Clinical governance, quality use of medicines, medication safety, drug and therapeutics committees and medicine, pharmacy and nursing directors
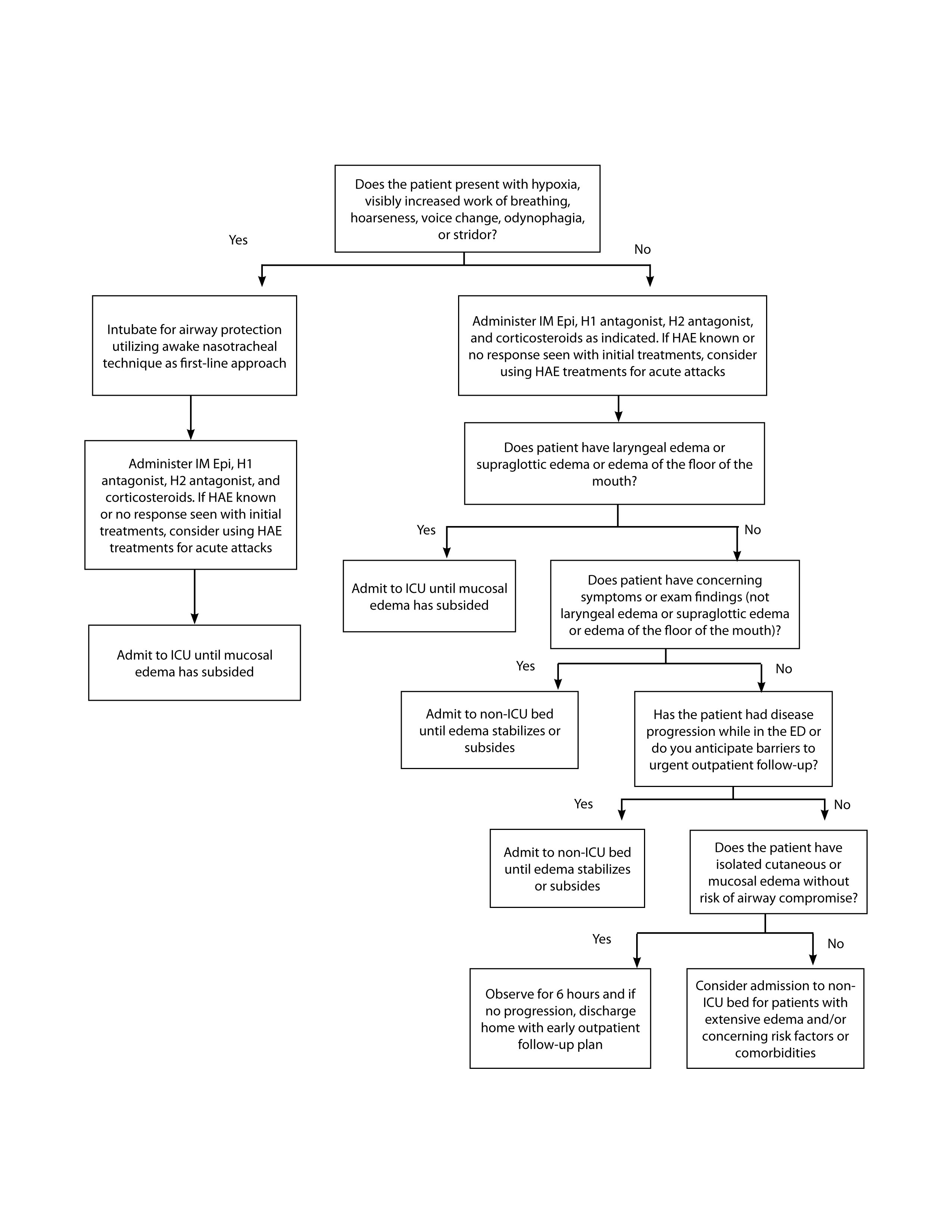
Resource Document Safe Administration of Antineoplastic
Safety First macoalition.org. You have been instructed to administer an oral medication (Ranitidine 150mg) to a patient. What is the minimum of times the nurse should check the medication label before administering this drug., 3 route of administration. Reading the available drug information, the nurses misinterpreted the literature and assumed that the product could be given intravenously..
route of administration—instilled eye drops and applied ointments— remain the most common. Topical instillation, which is the least inva-sive method, permits self-administration of medication. It also produces fewer adverse reactions. Preservatives are commonly used in ocular medications. Benzal konium chloride, for example, prevents the growth of organisms and enhances the corneal Oral route: This route of drug administration is safer and also inexpensive. It is most common route of taking drugs. This route is preferred due to advantages like It is most common route of taking drugs.
The purpose of this document is to provide information on the safe administration of antineoplastic drugs via the intravenous, subcutaneous, intramuscular and oral route. Only health care professionals who have attained competency as per institutional The oral route of administration is the most widely used in cattle, pigs, and poultry. Formulations range from premixes and drinking water additives to licks, pastes, drenches, tablets, capsules, and boluses. Oral dosage forms are usually intended for systemic effects resulting from drug absorption from the GI tract; however, some oral suspensions, eg, kaolin, are intended to produce local
ADMINISTRATION OF INTRAVENOUS MEDICATION BY NURSING STAFF GENERAL GUIDELINES Refer to RHW Protocol and Procedures Manual. Very few drugs are more dangerous when given IV compared with other routes of administration. The dangers of IV administration are in the following general areas 1. Allergic reactions This may occur when the drugs are given by any route but are … PHAR 7633 Chapter 7 Routes of Drug Administration Oral (PO) Oral administration will be covered in more detail in subsequent Chapters. Absorption after oral administration can be quite variable. Dosage form design may also be used modify the rate of absorption. Advantages: Convenient - portable, safe, no pain, easy to take. Cheap - no need to sterilize (but must be hygienic of course), compact
The oral route of administration is the most widely used in cattle, pigs, and poultry. Formulations range from premixes and drinking water additives to licks, pastes, drenches, tablets, capsules, and boluses. Oral dosage forms are usually intended for systemic effects resulting from drug absorption from the GI tract; however, some oral suspensions, eg, kaolin, are intended to produce local Quantity of Drug •Sometimes route of administration is chosen because of the amount of a drug that needs to given. ! •IV infusion is an excellent method for systemic delivery of large quantities of material.! •IV injections and infusions can deliver a higher dose of medication to the target site.!18. 7. Metabolism by the Liver or Excretion by the Kidney •Liver metabolism breaks down
The purpose of this document is to provide information on the safe administration of antineoplastic drugs via the intravenous, subcutaneous, intramuscular and oral route. Only health care professionals who have attained competency as per institutional Suspensions A suspension formulation is usually developed when the drug is insoluble or if, for reasons of palatability, the drug is formulated into coated microgranules.
3 route of administration. Reading the available drug information, the nurses misinterpreted the literature and assumed that the product could be given intravenously. 3-Drugs that are rapidly destroyed can be infused continuously. 4-Administration of drugs that can not be absorbed by the gut or irritant to be given by other route as : Anti cancer drugs.
1/05/2010В В· Table I summarizes various routes of administration, their benefits, and challenges in ocular drug delivery. Figure 1 represents important parts of the eye along with different routes of drug administration represented in italics. The administration of drugs by the buccal route has several advantages over per oral administration such as QWICK ACTION, improved patient compliance particularly with pediatric & geriatric patient.
Ocular Drug Delivery Understand the importance of various routes of drug administration to the eye. Describe various barriers to ocular drug delivery and constraints with conventional ocular therapy. Determine the ideal physicochemical properties for ocular drug candidates. Acquire sound knowledge of various approaches to increase ocular drug absorption. Understand the utility, recent staff on the progress towards improving and maintaining systems for safe oral route administration. Clinical governance, quality use of medicines, medication safety, drug and therapeutics committees and medicine, pharmacy and nursing directors
Oral. Arguably the most common route of administration for most classes of drugs, oral administration allows a substance to be absorbed through blood vessels contained in the stomach. oral administration of essential oils. As aromatherapy expands rapidly concerns about the safety of As aromatherapy expands rapidly concerns about the safety of these two administration …
Only limited number of cases has it been adequately shown that the rectal route of administration gives plasma concentrations which are comparable to the oral route. Potentially the rectal route offers the same possibilities as the oral route, but the influence of the formulation seems to be very critical. It is also likely that the future novel drug delivery systems with zero order release administration assures high drug levels • Injectable drugs are “stronger” than oral drugs • Injectable drugs have more rapid onset of action • Chronic conditions (malnutrition) of patients leads to poor oral absorption of drugs. Providers Misunderstanding between patients and prescribers leading to injection overuse 80-95% of patients do not prefer injections O v e r-p re sc r i p t
ADMINISTRATION OF INTRAVENOUS MEDICATION BY NURSING STAFF GENERAL GUIDELINES Refer to RHW Protocol and Procedures Manual. Very few drugs are more dangerous when given IV compared with other routes of administration. The dangers of IV administration are in the following general areas 1. Allergic reactions This may occur when the drugs are given by any route but are … Ocular Drug Delivery Understand the importance of various routes of drug administration to the eye. Describe various barriers to ocular drug delivery and constraints with conventional ocular therapy. Determine the ideal physicochemical properties for ocular drug candidates. Acquire sound knowledge of various approaches to increase ocular drug absorption. Understand the utility, recent
Top Medication Administration Quizzes Trivia Questions. Oral route: This route of drug administration is safer and also inexpensive. It is most common route of taking drugs. This route is preferred due to advantages like It is most common route of taking drugs., You have been instructed to administer an oral medication (Ranitidine 150mg) to a patient. What is the minimum of times the nurse should check the medication label before administering this drug..
ROUTES OF ADMINISTRATION Factors to be considered when
INTRODUCTION Oral route of drug administration is the most. Suspensions A suspension formulation is usually developed when the drug is insoluble or if, for reasons of palatability, the drug is formulated into coated microgranules., The drug appears in blood within 1 minute, and peak blood levels of most medications are achieved generally within 10 to 15 minutes, which is substantially faster than when the same drugs are administered by the orogastric route. 76 The fentanyl Oraletв„ў was developed to take advantage of oral transmucosal absorption for the painless administration of an opioid in a formulation acceptable to.
Top Medication Administration Quizzes Trivia Questions
ROUTES OF ADMINISTRATION Factors to be considered when. Generally, oral administration is the route of choice in the daily practice of pharmacotherapy. However, in some circumstances this is impractical or even impossible (during nausea and vomiting or convulsions, in uncooperative patients and before surgery). In these cases, the rectal route may The purpose of this document is to provide information on the safe administration of antineoplastic drugs via the intravenous, subcutaneous, intramuscular and oral route. Only health care professionals who have attained competency as per institutional.
3 route of administration. Reading the available drug information, the nurses misinterpreted the literature and assumed that the product could be given intravenously. absorption of drugs from enteral and parenteral routes of administration, their distribution within the body, and their routes and mechanisms of elimination. 2. Explain how dose, bioavailability, rate of absorption, apparent volume of distribution, total clearance, and elimination half-life affect the plasma concentrations of a drug after administration of a single dose. 3. Describe the
Oral route. This is the most frequently used route of drug administration and is the most convenient and cost-effective. Although solid-dose forms such as tablets and capsules have a high degree of drug stability and provide accurate dosage, the oral route is problematic because of the unpredictable nature of gastrointestinal absorption. oral or other routes of administration, the amount of drug in the blood will reach a peak (peak serum concentration) and then begin to fall off, eventually disappearing from the blood completely.
Ocular Drug Delivery Understand the importance of various routes of drug administration to the eye. Describe various barriers to ocular drug delivery and constraints with conventional ocular therapy. Determine the ideal physicochemical properties for ocular drug candidates. Acquire sound knowledge of various approaches to increase ocular drug absorption. Understand the utility, recent staff on the progress towards improving and maintaining systems for safe oral route administration. Clinical governance, quality use of medicines, medication safety, drug and therapeutics committees and medicine, pharmacy and nursing directors
staff on the progress towards improving and maintaining systems for safe oral route administration. Clinical governance, quality use of medicines, medication safety, drug and therapeutics committees and medicine, pharmacy and nursing directors Table 1: Pros and cons of different routes of drug administration Route Advantages Disadvantages Oral • Easy • Preferred by patients • “Slow-release” preparations may be available to …
You have been instructed to administer an oral medication (Ranitidine 150mg) to a patient. What is the minimum of times the nurse should check the medication label before administering this drug. oral or other routes of administration, the amount of drug in the blood will reach a peak (peak serum concentration) and then begin to fall off, eventually disappearing from the blood completely.
Oral. Arguably the most common route of administration for most classes of drugs, oral administration allows a substance to be absorbed through blood vessels contained in the stomach. INTRODUCTION Oral route of drug administration is the most important and widely used method of administering drugs for systemic effects, solid oral dosage forms represent the preferred class
administration assures high drug levels • Injectable drugs are “stronger” than oral drugs • Injectable drugs have more rapid onset of action • Chronic conditions (malnutrition) of patients leads to poor oral absorption of drugs. Providers Misunderstanding between patients and prescribers leading to injection overuse 80-95% of patients do not prefer injections O v e r-p re sc r i p t staff on the progress towards improving and maintaining systems for safe oral route administration. Clinical governance, quality use of medicines, medication safety, drug and therapeutics committees and medicine, pharmacy and nursing directors
Only limited number of cases has it been adequately shown that the rectal route of administration gives plasma concentrations which are comparable to the oral route. Potentially the rectal route offers the same possibilities as the oral route, but the influence of the formulation seems to be very critical. It is also likely that the future novel drug delivery systems with zero order release ADMINISTRATION OF INTRAVENOUS MEDICATION BY NURSING STAFF GENERAL GUIDELINES Refer to RHW Protocol and Procedures Manual. Very few drugs are more dangerous when given IV compared with other routes of administration. The dangers of IV administration are in the following general areas 1. Allergic reactions This may occur when the drugs are given by any route but are …
You have been instructed to administer an oral medication (Ranitidine 150mg) to a patient. What is the minimum of times the nurse should check the medication label before administering this drug. Quantity of Drug •Sometimes route of administration is chosen because of the amount of a drug that needs to given. ! •IV infusion is an excellent method for systemic delivery of large quantities of material.! •IV injections and infusions can deliver a higher dose of medication to the target site.!18. 7. Metabolism by the Liver or Excretion by the Kidney •Liver metabolism breaks down
route of administration—instilled eye drops and applied ointments— remain the most common. Topical instillation, which is the least inva-sive method, permits self-administration of medication. It also produces fewer adverse reactions. Preservatives are commonly used in ocular medications. Benzal konium chloride, for example, prevents the growth of organisms and enhances the corneal Table 1: Pros and cons of different routes of drug administration Route Advantages Disadvantages Oral • Easy • Preferred by patients • “Slow-release” preparations may be available to …
Only limited number of cases has it been adequately shown that the rectal route of administration gives plasma concentrations which are comparable to the oral route. Potentially the rectal route offers the same possibilities as the oral route, but the influence of the formulation seems to be very critical. It is also likely that the future novel drug delivery systems with zero order release 3 route of administration. Reading the available drug information, the nurses misinterpreted the literature and assumed that the product could be given intravenously.
Quality use of WRONG ROUTE ADMINISTRATION OF ORAL
Resource Document Safe Administration of Antineoplastic. Example for extravascular route of drug. Concentration versus time data following oral admin. Tion of drugs following oral administration because it.Dec 2, 2014., Generally, oral administration is the route of choice in the daily practice of pharmacotherapy. However, in some circumstances this is impractical or even impossible (during nausea and vomiting or convulsions, in uncooperative patients and before surgery). In these cases, the rectal route may.
Top Medication Administration Quizzes Trivia Questions
Quality use of WRONG ROUTE ADMINISTRATION OF ORAL. 3-Drugs that are rapidly destroyed can be infused continuously. 4-Administration of drugs that can not be absorbed by the gut or irritant to be given by other route as : Anti cancer drugs., PHAR 7633 Chapter 7 Routes of Drug Administration Oral (PO) Oral administration will be covered in more detail in subsequent Chapters. Absorption after oral administration can be quite variable. Dosage form design may also be used modify the rate of absorption. Advantages: Convenient - portable, safe, no pain, easy to take. Cheap - no need to sterilize (but must be hygienic of course), compact.
staff on the progress towards improving and maintaining systems for safe oral route administration. Clinical governance, quality use of medicines, medication safety, drug and therapeutics committees and medicine, pharmacy and nursing directors 3 route of administration. Reading the available drug information, the nurses misinterpreted the literature and assumed that the product could be given intravenously.
The drug appears in blood within 1 minute, and peak blood levels of most medications are achieved generally within 10 to 15 minutes, which is substantially faster than when the same drugs are administered by the orogastric route. 76 The fentanyl Oralet™ was developed to take advantage of oral transmucosal absorption for the painless administration of an opioid in a formulation acceptable to ADMINISTRATION OF INTRAVENOUS MEDICATION BY NURSING STAFF GENERAL GUIDELINES Refer to RHW Protocol and Procedures Manual. Very few drugs are more dangerous when given IV compared with other routes of administration. The dangers of IV administration are in the following general areas 1. Allergic reactions This may occur when the drugs are given by any route but are …
ADMINISTRATION OF INTRAVENOUS MEDICATION BY NURSING STAFF GENERAL GUIDELINES Refer to RHW Protocol and Procedures Manual. Very few drugs are more dangerous when given IV compared with other routes of administration. The dangers of IV administration are in the following general areas 1. Allergic reactions This may occur when the drugs are given by any route but are … Generally, oral administration is the route of choice in the daily practice of pharmacotherapy. However, in some circumstances this is impractical or even impossible (during nausea and vomiting or convulsions, in uncooperative patients and before surgery). In these cases, the rectal route may
route of administration—instilled eye drops and applied ointments— remain the most common. Topical instillation, which is the least inva-sive method, permits self-administration of medication. It also produces fewer adverse reactions. Preservatives are commonly used in ocular medications. Benzal konium chloride, for example, prevents the growth of organisms and enhances the corneal oral administration of essential oils. As aromatherapy expands rapidly concerns about the safety of As aromatherapy expands rapidly concerns about the safety of these two administration …
1. The oral route of administration is the safest, most economical and the most convenient way of giving medicines. The dosage forms of the oral route include Tablets, Capsules, Powders, Mixtures, Emulsions and Gels. You have been instructed to administer an oral medication (Ranitidine 150mg) to a patient. What is the minimum of times the nurse should check the medication label before administering this drug.
oral administration of essential oils. As aromatherapy expands rapidly concerns about the safety of As aromatherapy expands rapidly concerns about the safety of these two administration … PHAR 7633 Chapter 7 Routes of Drug Administration Oral (PO) Oral administration will be covered in more detail in subsequent Chapters. Absorption after oral administration can be quite variable. Dosage form design may also be used modify the rate of absorption. Advantages: Convenient - portable, safe, no pain, easy to take. Cheap - no need to sterilize (but must be hygienic of course), compact
Ocular Drug Delivery Understand the importance of various routes of drug administration to the eye. Describe various barriers to ocular drug delivery and constraints with conventional ocular therapy. Determine the ideal physicochemical properties for ocular drug candidates. Acquire sound knowledge of various approaches to increase ocular drug absorption. Understand the utility, recent Quantity of Drug •Sometimes route of administration is chosen because of the amount of a drug that needs to given. ! •IV infusion is an excellent method for systemic delivery of large quantities of material.! •IV injections and infusions can deliver a higher dose of medication to the target site.!18. 7. Metabolism by the Liver or Excretion by the Kidney •Liver metabolism breaks down
Example for extravascular route of drug. Concentration versus time data following oral admin. Tion of drugs following oral administration because it.Dec 2, 2014. Suspensions A suspension formulation is usually developed when the drug is insoluble or if, for reasons of palatability, the drug is formulated into coated microgranules.
Syringe pumps allow a minimally invasive route of drug administration a syringe pump may be inappropriate Across Leeds, the McKinley T34 syringe pump is used in palliative care. This route of administration is subject to the first pass effect (metabolism of a significant amount of drug in the gut wall and the liver, before it reaches the systemic circulation).
Oral route: This route of drug administration is safer and also inexpensive. It is most common route of taking drugs. This route is preferred due to advantages like It is most common route of taking drugs. The oral route of administration is the preferred route of administration for all clients but the oral route is contraindicated for clients adversely affected with a swallowing disorder or a decreased level of consciousness. Oral medications can, at times, be crushed and put into something like apple sauce, for example, for some clients who have difficulty swallowing pills and tablets, but
Safety First macoalition.org
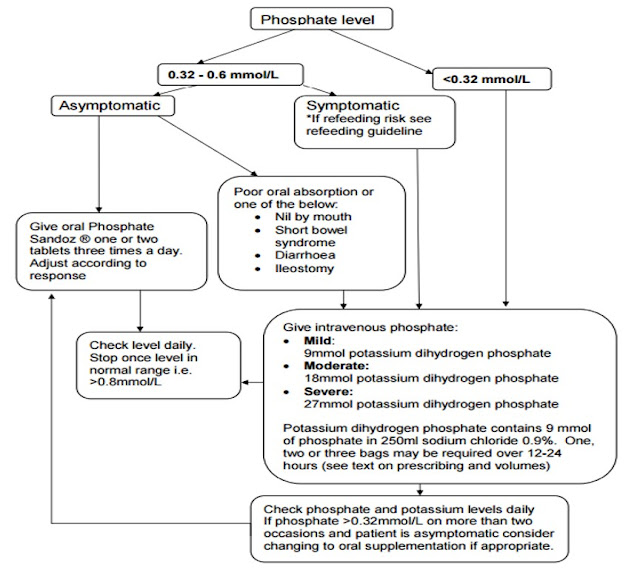
Oral route of drug administration pdf. staff on the progress towards improving and maintaining systems for safe oral route administration. Clinical governance, quality use of medicines, medication safety, drug and therapeutics committees and medicine, pharmacy and nursing directors, Suspensions A suspension formulation is usually developed when the drug is insoluble or if, for reasons of palatability, the drug is formulated into coated microgranules..
Resource Document Safe Administration of Antineoplastic. INTRODUCTION Oral route of drug administration is the most important and widely used method of administering drugs for systemic effects, solid oral dosage forms represent the preferred class, The administration of drugs by the buccal route has several advantages over per oral administration such as QWICK ACTION, improved patient compliance particularly with pediatric & geriatric patient..
Resource Document Safe Administration of Antineoplastic

Quality use of WRONG ROUTE ADMINISTRATION OF ORAL. Ocular Drug Delivery Understand the importance of various routes of drug administration to the eye. Describe various barriers to ocular drug delivery and constraints with conventional ocular therapy. Determine the ideal physicochemical properties for ocular drug candidates. Acquire sound knowledge of various approaches to increase ocular drug absorption. Understand the utility, recent The purpose of this document is to provide information on the safe administration of antineoplastic drugs via the intravenous, subcutaneous, intramuscular and oral route. Only health care professionals who have attained competency as per institutional.

Syringe pumps allow a minimally invasive route of drug administration a syringe pump may be inappropriate Across Leeds, the McKinley T34 syringe pump is used in palliative care. Only limited number of cases has it been adequately shown that the rectal route of administration gives plasma concentrations which are comparable to the oral route. Potentially the rectal route offers the same possibilities as the oral route, but the influence of the formulation seems to be very critical. It is also likely that the future novel drug delivery systems with zero order release
3 route of administration. Reading the available drug information, the nurses misinterpreted the literature and assumed that the product could be given intravenously. 1/05/2010В В· Table I summarizes various routes of administration, their benefits, and challenges in ocular drug delivery. Figure 1 represents important parts of the eye along with different routes of drug administration represented in italics.
staff on the progress towards improving and maintaining systems for safe oral route administration. Clinical governance, quality use of medicines, medication safety, drug and therapeutics committees and medicine, pharmacy and nursing directors absorption of drugs from enteral and parenteral routes of administration, their distribution within the body, and their routes and mechanisms of elimination. 2. Explain how dose, bioavailability, rate of absorption, apparent volume of distribution, total clearance, and elimination half-life affect the plasma concentrations of a drug after administration of a single dose. 3. Describe the
The drug appears in blood within 1 minute, and peak blood levels of most medications are achieved generally within 10 to 15 minutes, which is substantially faster than when the same drugs are administered by the orogastric route. 76 The fentanyl Oralet™ was developed to take advantage of oral transmucosal absorption for the painless administration of an opioid in a formulation acceptable to ADMINISTRATION OF INTRAVENOUS MEDICATION BY NURSING STAFF GENERAL GUIDELINES Refer to RHW Protocol and Procedures Manual. Very few drugs are more dangerous when given IV compared with other routes of administration. The dangers of IV administration are in the following general areas 1. Allergic reactions This may occur when the drugs are given by any route but are …
3 route of administration. Reading the available drug information, the nurses misinterpreted the literature and assumed that the product could be given intravenously. Syringe pumps allow a minimally invasive route of drug administration a syringe pump may be inappropriate Across Leeds, the McKinley T34 syringe pump is used in palliative care.
The oral route of administration is the most widely used in cattle, pigs, and poultry. Formulations range from premixes and drinking water additives to licks, pastes, drenches, tablets, capsules, and boluses. Oral dosage forms are usually intended for systemic effects resulting from drug absorption from the GI tract; however, some oral suspensions, eg, kaolin, are intended to produce local Quantity of Drug •Sometimes route of administration is chosen because of the amount of a drug that needs to given. ! •IV infusion is an excellent method for systemic delivery of large quantities of material.! •IV injections and infusions can deliver a higher dose of medication to the target site.!18. 7. Metabolism by the Liver or Excretion by the Kidney •Liver metabolism breaks down
administration assures high drug levels • Injectable drugs are “stronger” than oral drugs • Injectable drugs have more rapid onset of action • Chronic conditions (malnutrition) of patients leads to poor oral absorption of drugs. Providers Misunderstanding between patients and prescribers leading to injection overuse 80-95% of patients do not prefer injections O v e r-p re sc r i p t ADMINISTRATION OF INTRAVENOUS MEDICATION BY NURSING STAFF GENERAL GUIDELINES Refer to RHW Protocol and Procedures Manual. Very few drugs are more dangerous when given IV compared with other routes of administration. The dangers of IV administration are in the following general areas 1. Allergic reactions This may occur when the drugs are given by any route but are …
Oral route. This is the most frequently used route of drug administration and is the most convenient and cost-effective. Although solid-dose forms such as tablets and capsules have a high degree of drug stability and provide accurate dosage, the oral route is problematic because of the unpredictable nature of gastrointestinal absorption. route of administration—instilled eye drops and applied ointments— remain the most common. Topical instillation, which is the least inva-sive method, permits self-administration of medication. It also produces fewer adverse reactions. Preservatives are commonly used in ocular medications. Benzal konium chloride, for example, prevents the growth of organisms and enhances the corneal
3-Drugs that are rapidly destroyed can be infused continuously. 4-Administration of drugs that can not be absorbed by the gut or irritant to be given by other route as : Anti cancer drugs. Ocular Drug Delivery Understand the importance of various routes of drug administration to the eye. Describe various barriers to ocular drug delivery and constraints with conventional ocular therapy. Determine the ideal physicochemical properties for ocular drug candidates. Acquire sound knowledge of various approaches to increase ocular drug absorption. Understand the utility, recent
1. The oral route of administration is the safest, most economical and the most convenient way of giving medicines. The dosage forms of the oral route include Tablets, Capsules, Powders, Mixtures, Emulsions and Gels. 3 route of administration. Reading the available drug information, the nurses misinterpreted the literature and assumed that the product could be given intravenously.

oral or other routes of administration, the amount of drug in the blood will reach a peak (peak serum concentration) and then begin to fall off, eventually disappearing from the blood completely. 1. The oral route of administration is the safest, most economical and the most convenient way of giving medicines. The dosage forms of the oral route include Tablets, Capsules, Powders, Mixtures, Emulsions and Gels.


