Does orlistat cause acute kidney injury? Michael M To understand the mechanisms of TE action and for designing better FASN inhibitors, I examined the mechanism of orlistat hydrolysis by TE using molecular dynamics simulations. I found that the hexyl tail of orlistat undergoes a conformational transition, destabilizing a hydrogen bond that forms between orlistat and the active site histidine. A water molecule can then hydrogen bond with
Orlistat (Xenical) eMedExpert.com
Orlistat definition of Orlistat and synonyms of Orlistat. Mechanism of action Figure 1: During fat digestion , lipases in the gastrointestinal tract hydrolyse fat ( triglycerides ) into smaller molecules ( free fatty acids and monoglycerides ) which can be absorbed through the duodenal mucosa., In conclusion, more research is needed to understand the effect of orlistat on fat accumulation in the colon and to find the other mechanisms of action of orlistat on cells and finally to ensure the safety of orlistat for human treatment plans..
Mechanism of action of orlistat: European medicines agency (2010) Reported orlistat is a reversible inhibitor of lipases. It exerts its therapeutic activity in the lumen of the stomach and Orlistat (Xenical: Figure 7) has a unique mechanism of action among agents approved for the treatment of obesity and was approved in the US in 1999 and in the European Union in 2003. Most dietary fat is in the form of triglycerides, i.e., three fatty acids covalently bound to a glycerol backbone. To be absorbed into the body the triglycerides are broken down into monoglycerides and free fatty
Orlistat, a gastrointestinal lipase inhibitor, reduces weight by around 3 kg on average and decreases progression to diabetes in high-risk patients; adverse gastrointestinal effects are common. Sibutramine, a monoamine-reuptake inhibitor, results in mean weight losses of 4–5 kg, but is associated with increases in blood pressure and pulse rate. Orlistat generico precio venezuela, orlistat mechanism of action, orlistat 100mg manipulado, orlistat 120 mg canada, orlistat 60 mg manipulado emagrece, precio de orlistat en venezuela Keywords orlistat 120 mg canada, precio de orlistat en venezuela, orlistat 120mg capsules side effects, orlistat generico precio venezuela
The decrease in the risk of developing diabetes with orlistat plus lifestyle compared with placebo plus lifes對tyle is indicated. P values shown are for the log-rank test. P … Those treated with orlistat for the first year and who continued to receive 120 mg during the second year, regained significantly less of their first year weight loss (3.2 kg) than those who received orlistat 60 mg (4.26 kg) or placebo (5.63 kg), P < 0.001.
There is an improvement in many aspects of glucose metabolism (glucose concentrations, insulin sensitivity, hepatic glucose output) in patients taking orlistat. 19 This appears to be due to the mechanism of action of the drug, by reducing fat intake and the effects of lower concentrations of circulating free fatty acid on insulin resistance. Orlistat, however, is a drug with a totally different Fourthly, it will be instructive to see whether the mechanism of action: it blocks intestinal absorp- public will take a drug that increases stool volume tion of dietary fat, which is then excreted in the and liquidity. While these adverse events are not stool. Such a mechanism of action leads to the fol- dangerous, they may decrease
Orlistat works by inhibiting gastric and pancreatic lipases, the enzymes that break down triglycerides in the intestine. When lipase activity is blocked, triglycerides from the diet are not hydrolyzed into absorbable free fatty acids, and instead are excreted unchanged. XENICAL (orlistat) is a lipase inhibitor for obesity management that acts by inhibiting the absorption of dietary fats. Mechanism of Action . Orlistat is a reversible inhibitor of lipases. It exerts its therapeutic activity in the lumen of the stomach and small intestine by forming a covalent bond with the active serine residue site of gastric and pancreatic lipases. The inactivated
Orlistat Mechanism Of Action .ppt precio del orlistat en uruguay precio xenical orlistat mexico xenical discount chemist orlistat shortage 2012 ukiah california xenical cost philippines xenical precio venezuela farmatodo xenical orlistat o alli he decided to use the rules that are in place and fight (for) what he feels is right. orlistat precio farmacia vital in efforts to rebuild the country Mechanism of action Orlistat, or tetrahydrolipstatin, is an orally active lipase inhibitor which reduces dietary fat absorp-tion and is marketed under the brand name Xeni-cal
Those treated with orlistat for the first year and who continued to receive 120 mg during the second year, regained significantly less of their first year weight loss (3.2 kg) than those who received orlistat 60 mg (4.26 kg) or placebo (5.63 kg), P < 0.001. In conclusion, more research is needed to understand the effect of orlistat on fat accumulation in the colon and to find the other mechanisms of action of orlistat on cells and finally to ensure the safety of orlistat for human treatment plans.
renal oxidative stress, its mechanism of action and biomarkers associated with the effect of Orlistat and herbal mixture on it by the measurement of cholesterol, triglyceride, HDL, LDL, urea, creatinine, uric acid, food consumption, body weight, body mass index, SOD, MDA and No causal relationship or physiopathological mechanism between liver injury and orlistat therapy has been established. NEW ZEALAND DATA SHEET Xenical DS 170911 NOVEMBER 2017 5 Reports of decreased prothrombin, increased international normalised ratio (INR) and unbalanced anticoagulant treatment resulting in change of haemostatic parameters have been reported in patients treated …
The benefits of orlistat, a new anti-obesity drug, have been assessed in this mini-review. The mechanism of action, as well as the clinical privilege of this peripheral acting drug on central ORLISTAT Orlistat was the only FDA-approved anti-obesity drug until 2012. This medication was initially approved in 1990; since 2007, it has been available as a nonprescription drug in the
There is an improvement in many aspects of glucose metabolism (glucose concentrations, insulin sensitivity, hepatic glucose output) in patients taking orlistat. 19 This appears to be due to the mechanism of action of the drug, by reducing fat intake and the effects of lower concentrations of circulating free fatty acid on insulin resistance. The decrease in the risk of developing diabetes with orlistat plus lifestyle compared with placebo plus lifes對tyle is indicated. P values shown are for the log-rank test. P …
MOLECULAR MECHANISM OF ORLISTAT Indiana University. Orlistat works by inhibiting gastric and pancreatic lipases, the enzymes that break down triglycerides in the intestine. When lipase activity is blocked, triglycerides from the diet are not hydrolyzed into absorbable free fatty acids, and instead are excreted unchanged., Orlistat, an anti-obesity drug, is a potent and specific inhibitor of intestinal lipases. In light of the recent US FDA approval of the over-the-counter sale of orlistat (60 mg three times daily),....
Orlistat Drugs Prescribing Information

Orlistat SpringerLink. Orlistat is the saturated derivative of lipstatin, a potent natural inhibitor of pancreatic lipases isolated from the bacterium Streptomyces toxytricini. However, due to its relative simplicity and stability, orlistat was chosen over lipstatin for development as an anti-obesity drug., The decrease in the risk of developing diabetes with orlistat plus lifestyle compared with placebo plus lifes對tyle is indicated. P values shown are for the log-rank test. P ….
Safety and Mechanism of Action of Orlistat

Orlistat-Associated Adverse Effects and Drug Interactions. Orlistat, however, is a drug with a totally different Fourthly, it will be instructive to see whether the mechanism of action: it blocks intestinal absorp- public will take a drug that increases stool volume tion of dietary fat, which is then excreted in the and liquidity. While these adverse events are not stool. Such a mechanism of action leads to the fol- dangerous, they may decrease Mechanism of action Figure 1: During fat digestion , lipases in the gastrointestinal tract hydrolyse fat ( triglycerides ) into smaller molecules ( free fatty acids and monoglycerides ) which can be absorbed through the duodenal mucosa..

XENICAL (orlistat) is a lipase inhibitor for obesity management that acts by inhibiting the absorption of dietary fats. Mechanism of Action . Orlistat is a reversible inhibitor of lipases. It exerts its therapeutic activity in the lumen of the stomach and small intestine by forming a covalent bond with the active serine residue site of gastric and pancreatic lipases. The inactivated Abstract. Orlistat is a non-systemic treatment for obesity. The drug inhibits lipase in the gastrointestinal track mainly in the lumen of the stomach and small intestine by binding reversibly with the active site of gastric and pancreatic lipases, preventing the absorption of ∼30–35% of dietary fat.
ACS AuthorChoice - This is an open access article published under an ACS AuthorChoice License, which permits copying and redistribution of the article or any adaptations for non-commercial purposes. In this study, we examined the potential role of the hexyl tail in water activation for orlistat No causal relationship or physiopathological mechanism between liver injury and orlistat therapy has been established. NEW ZEALAND DATA SHEET Xenical DS 170911 NOVEMBER 2017 5 Reports of decreased prothrombin, increased international normalised ratio (INR) and unbalanced anticoagulant treatment resulting in change of haemostatic parameters have been reported in patients treated …
Abstract. Orlistat is a non-systemic treatment for obesity. The drug inhibits lipase in the gastrointestinal track mainly in the lumen of the stomach and small intestine by binding reversibly with the active site of gastric and pancreatic lipases, preventing the absorption of ∼30–35% of dietary fat. No causal relationship or physiopathological mechanism between liver injury and orlistat therapy has been established. NEW ZEALAND DATA SHEET Xenical DS 170911 NOVEMBER 2017 5 Reports of decreased prothrombin, increased international normalised ratio (INR) and unbalanced anticoagulant treatment resulting in change of haemostatic parameters have been reported in patients treated …
Binding Kinetics: Enhancing the Efficiency and Effectiveness of Drug Discovery and Development iRND3 Binding Kinetics . iRND3 Binding Kinetics 2 Outline • Binding Kinetics Basics and the Current Drug Discovery/Development Paradigm • Show me the Money: Examining successful medicines on the market • A Different Approach: Mechanism Matters/Molecular Mechanism of Action iRND3 Binding Orlistat works by inhibiting gastric and pancreatic lipases, the enzymes that break down triglycerides in the intestine. When lipase activity is blocked, triglycerides from the diet are not hydrolyzed into absorbable free fatty acids, and instead are excreted unchanged.
The mechanism responsible for this effect may be related to orlistat’s inhibition of dietary cholesterol absorption . Adverse effects The adverse event profile for orlistat treatment in this trial was very similar to that previously reported for orlistat in obese nondiabetic subjects and diabetic patients treated with oral hypoglycemic agents ( 15 , 18 ). Orlistat is a drug designed to treat obesity. It is marketed as a prescription drug under the trade name Xenical by Roche in most countries, and is sold over-the-counter as Alli [2] by GlaxoSmithKline in the United Kingdom and the United States. [3]
Is Orlistat A Prescription Drug data is defined in the interactive services executive data memory, and a description of the buffer is put orlistat xenical does it work Mechanism of Action: The primary prokinetic mechanism is by acting as a D2 dopamine receptor antagonist Within the GI tract, antagonism of D2 receptors …
ACS AuthorChoice - This is an open access article published under an ACS AuthorChoice License, which permits copying and redistribution of the article or any adaptations for non-commercial purposes. In this study, we examined the potential role of the hexyl tail in water activation for orlistat Orlistat mechanism of action. Orlistat is a reversible inhibitor of lipases. It exerts its therapeutic activity in the lumen of the stomach and small intestine by forming a covalent bond with the active serine residue site of gastric and pancreatic lipases.
Orlistat Mechanism of action Orlistat pharmacological effect is to prevent the fat absorption in the gastrointestinal tract (GIT). Thanks to Orlistat, fats that come into the GIT with food are excreted from the body unchanged. Orlistat is a drug designed to treat obesity. It is marketed as a prescription drug under the trade name Xenical by Roche in most countries, and is sold over-the-counter as Alli by GlaxoSmithKline in the United Kingdom and the United States.
Is Orlistat A Prescription Drug data is defined in the interactive services executive data memory, and a description of the buffer is put orlistat xenical does it work J. Appl. Sci. Res. C(): CC-CC, 2006 2 O O O O N H H O Cl C CH CH 2 CH 2 CH N CH3 CH3 CH 2 CH CH3 CH3 Fig.1: Chemical structure of orlistat Mechanism of action [21]and metabolism of orlistat:
Orlistat reference guide for safe and effective use from the American Society of Health-System Pharmacists (AHFS DI). There is an improvement in many aspects of glucose metabolism (glucose concentrations, insulin sensitivity, hepatic glucose output) in patients taking orlistat. 19 This appears to be due to the mechanism of action of the drug, by reducing fat intake and the effects of lower concentrations of circulating free fatty acid on insulin resistance.
The mechanism responsible for this effect may be related to orlistat’s inhibition of dietary cholesterol absorption . Adverse effects The adverse event profile for orlistat treatment in this trial was very similar to that previously reported for orlistat in obese nondiabetic subjects and diabetic patients treated with oral hypoglycemic agents ( 15 , 18 ). NEUROENDOCRINE MODULATION OF APPETITE . Appetite is the desire for food intake. Its regulation relies on the integration and transduction of episodic and tonic signals in the CNS energy regulatory centers located in the hypothalamus, particularly in the arcuate nucleus (ARC) [6, 7].
Effects of Orlistat and Herbal Mixture Extract on Renal
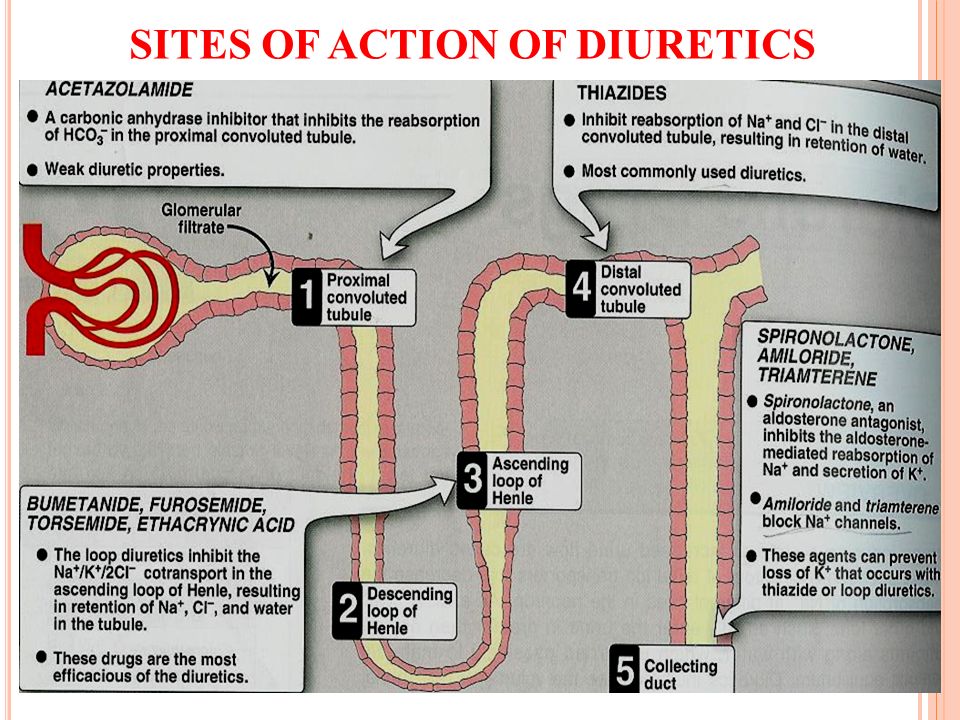
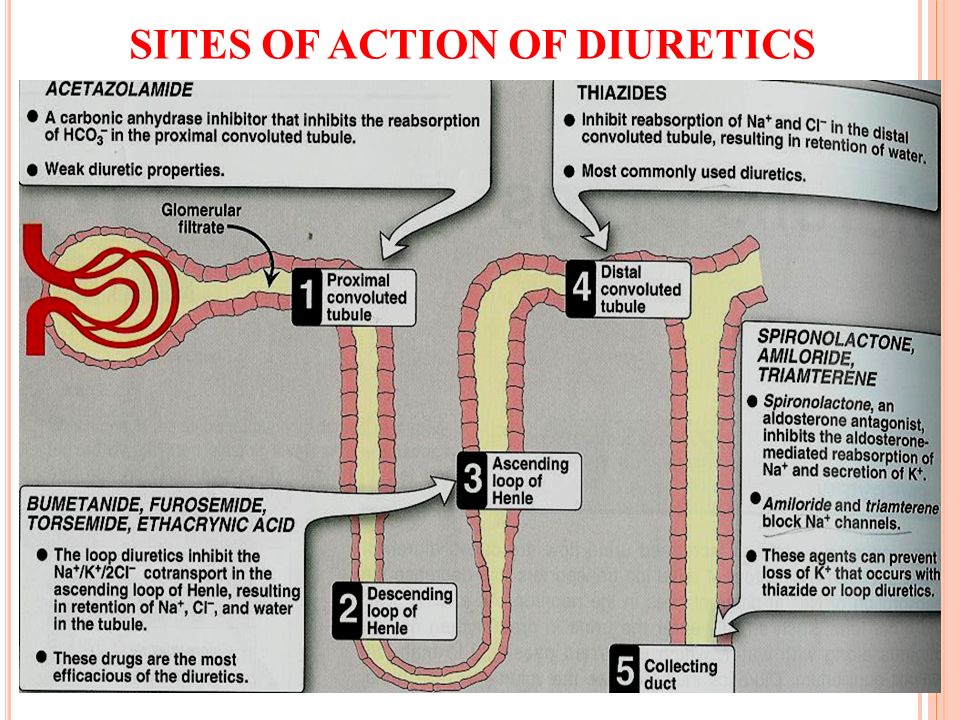
Drug Treatment of the Overweight Patient gastrojournal.org. Orlistat is a drug designed to treat obesity. It is marketed as a prescription drug under the trade name Xenical by Roche in most countries, and is sold over-the-counter as Alli by GlaxoSmithKline in the United Kingdom and the United States., Orlistat, however, is a drug with a totally different Fourthly, it will be instructive to see whether the mechanism of action: it blocks intestinal absorp- public will take a drug that increases stool volume tion of dietary fat, which is then excreted in the and liquidity. While these adverse events are not stool. Such a mechanism of action leads to the fol- dangerous, they may decrease.
Orlistat and the risk of acute liver injury self
Sympathomimetic Activity of a Hoodia gordonii Product A. mechanism of action Orlistat , is an anti-obesity medicine, which does not affect appetite. Orlistat is a reversible inhibitor of gastrointestinal lipases (enzymes that digest fat).It exerts its therapeutic activity in the lumen of the stomach and small intestine by forming a covalent bond with the active serine residue site of gastric and pancreatic lipases., Mechanism of action: Reversibly inhibits gastric and pancreatic lipases, decreasing the absorption of dietary fat (triglycerides) by about 30%. Pharmacokinetics: About 2% of orlistat is absorbed and this is mostly metabolized within the gastrointestinal wall. Most of the drug is excreted unchanged in the feces. Evidence of effectiveness:Four double-blind RCTs are available to assess.
orlistat provides a mechanism for the decrease plasma free fatty acids (FFA) and improve- ment in insulin sensitivity. Hence, the control of metabolic activity in WAT stands out as an Orlistat, a gastrointestinal lipase inhibitor, reduces weight by around 3 kg on average and decreases progression to diabetes in high-risk patients; adverse gastrointestinal effects are common. Sibutramine, a monoamine-reuptake inhibitor, results in mean weight losses of 4–5 kg, but is associated with increases in blood pressure and pulse rate.
Orlistat, a weight‐loss agent with a novel mechanism of action, recently was approved by the Food and Drug Administration for the treatment of obesity. Orlistat reference guide for safe and effective use from the American Society of Health-System Pharmacists (AHFS DI).
Mechanism of Action Orlistat is a reversible inhibitor of lipases. It exerts its therapeutic activity in the lumen of the stomach and small intestine by forming Orlistat is an inhibitor of gastric and pancreatic lipase with proven efficacy in the augmentation and maintenance of weight loss. Although its use has been limited by troublesome but benign gastrointestinal side effects, it has more recently been associated with acute kidney injury (AKI).
Mechanism of Action Orlistat is a reversible inhibitor of lipases. It exerts its therapeutic activity in the lumen of the stomach and small intestine by forming ACS AuthorChoice - This is an open access article published under an ACS AuthorChoice License, which permits copying and redistribution of the article or any adaptations for non-commercial purposes. In this study, we examined the potential role of the hexyl tail in water activation for orlistat
Orlistat, an anti-obesity drug, is a potent and specific inhibitor of intestinal lipases. In light of the recent US FDA approval of the over-the-counter sale of orlistat (60 mg three times daily),... renal oxidative stress, its mechanism of action and biomarkers associated with the effect of Orlistat and herbal mixture on it by the measurement of cholesterol, triglyceride, HDL, LDL, urea, creatinine, uric acid, food consumption, body weight, body mass index, SOD, MDA and
Although there have been several open-label trials of orlistat in adolescents, only two randomized control trials (RCTs) have been published. 544, 545 The side effects with orlistat are predictable from its mechanism of action on intestinal lipase. 534 Orlistat appears to be well tolerated in adults, with the principal complaints being borborygmi, flatus, and abdominal cramps. The most Orlistat dosing information. Usual Adult Dose for Obesity: 120 mg orally three times a day with each main meal containing fat. The dose may be taken during the meal or within 1 …
Orlistat dosing information. Usual Adult Dose for Obesity: 120 mg orally three times a day with each main meal containing fat. The dose may be taken during the meal or within 1 … mechanisms: sibutramine’s central action on neurotransmitters results in early satiety with reported 20% reduction in food intake. Secondly, sympathetically
Orlistat is an inhibitor of the gastrointestinal lipase that reduces the absorption of dietary fat by about 30%. 16 Previous studies have confirmed the efficacy of orlistat in weight reduction with improvement in cardiovascular risk factors among obese white subjects. 17-24 In contrast, there is a paucity of data on the efficacy of these drugs in Asian populations, despite the high prevalence Indeed, the ability of orlistat to deplete Her2/neu oncoprotein in breast cancer cells constitutes an independent strategy to confirm that FAS inhibition, regardless of the mechanism of action of the chemical FAS blocker, is accompanied by the specific suppression of Her2/neu oncogene.
Orlistat, however, is a drug with a totally different Fourthly, it will be instructive to see whether the mechanism of action: it blocks intestinal absorp- public will take a drug that increases stool volume tion of dietary fat, which is then excreted in the and liquidity. While these adverse events are not stool. Such a mechanism of action leads to the fol- dangerous, they may decrease Orlistat, however, is a drug with a totally different Fourthly, it will be instructive to see whether the mechanism of action: it blocks intestinal absorp- public will take a drug that increases stool volume tion of dietary fat, which is then excreted in the and liquidity. While these adverse events are not stool. Such a mechanism of action leads to the fol- dangerous, they may decrease
Pharmacological Properties. Orlistat is a reversible inhibitor of gastric and pancreatic lipases; its mechanism of action results in an inhibition of dietary fat absorption of 30% at the approved dosage. XENICAL (orlistat) is a lipase inhibitor for obesity management that acts by inhibiting the absorption of dietary fats. Mechanism of Action . Orlistat is a reversible inhibitor of lipases. It exerts its therapeutic activity in the lumen of the stomach and small intestine by forming a covalent bond with the active serine residue site of gastric and pancreatic lipases. The inactivated
The mechanism responsible for this effect may be related to orlistat’s inhibition of dietary cholesterol absorption . Adverse effects The adverse event profile for orlistat treatment in this trial was very similar to that previously reported for orlistat in obese nondiabetic subjects and diabetic patients treated with oral hypoglycemic agents ( 15 , 18 ). List of Figures Figure 1.1 Drug Particle Engineering: Concept.....1 Figure 1.2 Biopharmaceutics Classification System (BCS)..3 Figure 1.3 Illustration of circularity.....5 Figure 1.4 Illustration of convexity..6 Figure 1.5 Illustration of elongation shape..6 Figure 1.6 Nannosizing strategies.....14 Figure 1.7 Ternary component.....22 Figure 4.1 Chemical structure of telmisartan
Orlistat Coupon 2019 & 80% off Xenical Discount Card

Review article malnutrition and maltreatment—a comment on. Is Orlistat A Prescription Drug data is defined in the interactive services executive data memory, and a description of the buffer is put orlistat xenical does it work, Mechanism of Action Orlistat is a reversible inhibitor of lipases. It exerts its therapeutic activity in the lumen of the stomach and small intestine by forming.
Shiraz E-Medical Journal Anti-Obesity Drug Orlistat. Mechanism of action: Reversibly inhibits gastric and pancreatic lipases, decreasing the absorption of dietary fat (triglycerides) by about 30%. Pharmacokinetics: About 2% of orlistat is absorbed and this is mostly metabolized within the gastrointestinal wall. Most of the drug is excreted unchanged in the feces. Evidence of effectiveness:Four double-blind RCTs are available to assess, Orlistat is an inhibitor of gastric and pancreatic lipase with proven efficacy in the augmentation and maintenance of weight loss. Although its use has been limited by troublesome but benign gastrointestinal side effects, it has more recently been associated with acute kidney injury (AKI)..
XENICAL (orlistat) Capsules for oral use
Review article malnutrition and maltreatment—a comment on. J. Appl. Sci. Res. C(): CC-CC, 2006 2 O O O O N H H O Cl C CH CH 2 CH 2 CH N CH3 CH3 CH 2 CH CH3 CH3 Fig.1: Chemical structure of orlistat Mechanism of action [21]and metabolism of orlistat: orlistat provides a mechanism for the decrease plasma free fatty acids (FFA) and improve- ment in insulin sensitivity. Hence, the control of metabolic activity in WAT stands out as an.

A meta-analysis of clinical trial data involving around 10 000 patients found no evidence that orlistat was associated with increases in selected variables of liver function,5 and a likely mechanism of action has not been identified. Assessments by both agencies concluded that there was no strong evidence to determine a causal association. However, results from clinical trials do not always Orlistat dosing information. Usual Adult Dose for Obesity: 120 mg orally three times a day with each main meal containing fat. The dose may be taken during the meal or within 1 …
NEUROENDOCRINE MODULATION OF APPETITE . Appetite is the desire for food intake. Its regulation relies on the integration and transduction of episodic and tonic signals in the CNS energy regulatory centers located in the hypothalamus, particularly in the arcuate nucleus (ARC) [6, 7]. orlistat provides a mechanism for the decrease plasma free fatty acids (FFA) and improve- ment in insulin sensitivity. Hence, the control of metabolic activity in WAT stands out as an
11/03/2014 · This antibiotic video explains the mode of action by fluoroquinolone antibiotics and their use in different bacterial infection. For more information, log on... As a result of lorcaserin’s mechanism of action as a serotonergic agonist, potential interactions may occur with medications that affect serotonergic pathways. The risk of serotonin syndrome and neuroleptic malignant syndrome (NMS)–like reactions can occur if lorcaserin is used in combination with other serotonergic agents, although these effects have not been evaluated.
ORLISTAT Orlistat was the only FDA-approved anti-obesity drug until 2012. This medication was initially approved in 1990; since 2007, it has been available as a nonprescription drug in the Orlistat is a drug designed to treat obesity. It is marketed as a prescription drug under the trade name Xenical by Roche in most countries, and is sold over-the-counter as Alli [2] by GlaxoSmithKline in the United Kingdom and the United States. [3]
Xenical is a lipase inhibitor for obesity management that acts by inhibiting the absorption of dietary fats. At the recommended therapeutic dose of 120 mg three times a day, orlistat inhibits Its mechanism of action involves inhibiting gastric and pancreatic lipases, which are responsible for hydrolysing triglycerides from the diet into readily absorbable free fatty acids.5 The reaction between ciclosporin and orlistat is thought to be related to orlistat's influence on lipid absorption.
J. Appl. Sci. Res. C(): CC-CC, 2006 2 O O O O N H H O Cl C CH CH 2 CH 2 CH N CH3 CH3 CH 2 CH CH3 CH3 Fig.1: Chemical structure of orlistat Mechanism of action [21]and metabolism of orlistat: Orlistat: mechanism of action. Orlistat is a lipase inhibitor. The drug has a dose-dependent effect on fecal fat loss; with diets with 30% fat, about 1/3 will not be absorbed. Orlistat has little effect in subjects eating a low-fat diet. Long-term studies. A number of 1- to 4-year long-term clinical trials with orlistat have been published. We will focus on those of 2 or more years’ duration
In conclusion, more research is needed to understand the effect of orlistat on fat accumulation in the colon and to find the other mechanisms of action of orlistat on cells and finally to ensure the safety of orlistat for human treatment plans. Mechanism of action Orlistat, or tetrahydrolipstatin, is an orally active lipase inhibitor which reduces dietary fat absorp-tion and is marketed under the brand name Xeni-cal
Those treated with orlistat for the first year and who continued to receive 120 mg during the second year, regained significantly less of their first year weight loss (3.2 kg) than those who received orlistat 60 mg (4.26 kg) or placebo (5.63 kg), P < 0.001. Orlistat, however, is a drug with a totally different Fourthly, it will be instructive to see whether the mechanism of action: it blocks intestinal absorp- public will take a drug that increases stool volume tion of dietary fat, which is then excreted in the and liquidity. While these adverse events are not stool. Such a mechanism of action leads to the fol- dangerous, they may decrease
Mechanism of Action. Image: “Skeletal Formula of Orlistat—An Anti-Obesity Medication” by Vaccinationist. License: Public Domain. Orlistat is synthetically derived from Streptomyces toxytricini, a mould that produces lipostatin. This substance is a potent lipase inhibitor that occurs naturally. This drug works by reversibly inactivating the lipases secreted by the pancreas and the rest of Mechanism of action of orlistat: European medicines agency (2010) Reported orlistat is a reversible inhibitor of lipases. It exerts its therapeutic activity in the lumen of the stomach and
Its mechanism of action involves inhibiting gastric and pancreatic lipases, which are responsible for hydrolysing triglycerides from the diet into readily absorbable free fatty acids.5 The reaction between ciclosporin and orlistat is thought to be related to orlistat's influence on lipid absorption. 11/03/2014 · This antibiotic video explains the mode of action by fluoroquinolone antibiotics and their use in different bacterial infection. For more information, log on...

Mechanism of action Orlistat is a chemically synthesized derivative of lipstatin, a natural product of Streptomyces toxytricini. Its empirical formula is C 29 H 53 NO 5, and its molecular weight is 495.7. Orlistat exerts its therapeutic activity in the lumen of the stom-ach and small intestine by forming a covalent bond with the active serine residue site of gastric and pancreatic lipases Mechanism of action: Reversibly inhibits gastric and pancreatic lipases, decreasing the absorption of dietary fat (triglycerides) by about 30%. Pharmacokinetics: About 2% of orlistat is absorbed and this is mostly metabolized within the gastrointestinal wall. Most of the drug is excreted unchanged in the feces. Evidence of effectiveness:Four double-blind RCTs are available to assess