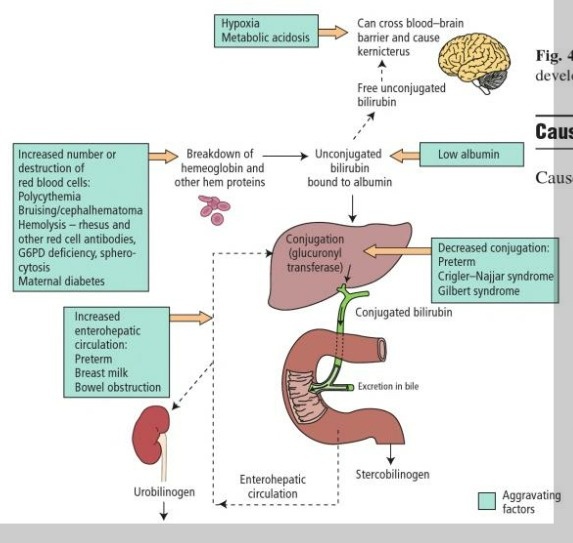
Mineral Nitrogen In The Plant-Soil System 1st Edition The photosynthetic capacity of leaves is related to the nitrogen content primarily bacause the proteins of the Calvin cycle and thylakoids represent the majority of leaf nitrogen. To a first approximation, thylakoid nitrogen is proportional to the chlorophyll content (50 mol thylakoid N mol-1 Chl
Review Nitrogen Fixing Microorganisms
The nitrogen cycle (article) Ecology Khan Academy. To be useful to plants, nitrogen must be converted into active forms. Natural events such as lightning and cosmic radiation create nitrates in the atmosphere, which are then brought out of the atmosphere and to the ground by precipitation (rain, snow, sleet, etc.). This process of nitrate formation is known as nitrogen fixation. There are two types of nitrogen fixation:, Role of Nitrogen in Plants: Nitrogen is a universally occurring element in all the living beings. Apart from water and mineral salts the next major substance in plant cell is protein (about 10-12% of the cell)..
To be useful to plants, nitrogen must be converted into active forms. Natural events such as lightning and cosmic radiation create nitrates in the atmosphere, which are then brought out of the atmosphere and to the ground by precipitation (rain, snow, sleet, etc.). This process of nitrate formation is known as nitrogen fixation. There are two types of nitrogen fixation: Plants deficient in nitrogen do not show the retranslocation of zinc from the older leaves, indicating that the deficiency symptoms of zinc are more pronounced in the nitrogen deficient plants. Using zinc in the fertility program Both soil and leaf tissue tests are accurate evaluations of zinc requirements. If a crop is “zinc responsive” and a high yield program is being used, some zinc is
Urea plays a role as primary nitrogen source taken up actively by plants from the soil solution but is also an intermediate of plant arginine catabolism involved in nitrogen … what makes plants grow. OBJECTIVES: For youth to: identify five basic plant needs. describe what a plant needs in order to manufacture its own food. describe how the nutrient content of a soil can be improved. describe a plants role in the hydrologic cycle. identify way plants compete. associate plants habitats with plant needs. LESSON TIME: Lesson time may vary based upon learning activities
plants and enables them to extract nutrients from the soil. Phosphorus also plays a critical role in cell development and DNA formation. Insufficient soil P can result in delayed crop maturity, reduced flower development, low seed quality, and decreased crop yield. Too much P, on the other hand, can be harmful in some situations; when P levels increase in fresh water streams and lakes, algae In non-nitrogen-fixing plants, the xylem-nitrogen is found mainly in the form of nitrate and amino acids, whereas in nitrogen-fixing plants it contains mainly ureide nitrogen and the relative abundance of ureides in sap can be used as an indication of nitrogen activity.
Plants deficient in nitrogen do not show the retranslocation of zinc from the older leaves, indicating that the deficiency symptoms of zinc are more pronounced in the nitrogen deficient plants. Using zinc in the fertility program Both soil and leaf tissue tests are accurate evaluations of zinc requirements. If a crop is “zinc responsive” and a high yield program is being used, some zinc is In non-nitrogen-fixing plants, the xylem-nitrogen is found mainly in the form of nitrate and amino acids, whereas in nitrogen-fixing plants it contains mainly ureide nitrogen and the relative abundance of ureides in sap can be used as an indication of nitrogen activity.
In non-nitrogen-fixing plants, the xylem-nitrogen is found mainly in the form of nitrate and amino acids, whereas in nitrogen-fixing plants it contains mainly ureide nitrogen and the relative abundance of ureides in sap can be used as an indication of nitrogen activity. 7 Chapter 1-Introduction Nitrogen (N) is an essential macronutrient required by plants. Nitrogen is often a limiting component in high-input monoculture agricultural systems, despite the extensive use of …
Potassium, Calcium,Magnesium-How They Relate to Plant Growth by CARL SCHWARTZKOPF, Mid-Continent Agronomist, USGA Green Section Potassium, calcium and magnesium play an important role in soil-plant relationships. These elements are not only essential to the complex biochemistry of plant growth, but their pres- ence in the soil in adequate amounts and in suitable proportions to one another … Functions of nitrogen in plants Nitrogen is an essential element of all amino acids. Amino acids are the building blocks of proteins. Nitrogen is also a component of nucleic acids, which form the DNA of all living things and holds the genetic code. Nitrogen is a component of chlorophyll, which is the site of carbohydrate formation (photosynthesis). Chlorophyll is also the substance that gives
’Understanding Potassium and its Use in Agriculture’ explains the importance of potassium in plant nutrition and the diet of humans and animals, and describes the role of potassium based fertilizers in European agriculture. Thus, nitrogen supply to the plant will influence the amount of protein, amino acids, protoplasm and chlorophyll formed. Therefore, adequate supply of nitrogen is necessary to achieve high yield potential in crop. The atmosphere comprises of ~78% nitrogen as an inert, in unavailable form. Above every hectare of ground there are ~80000 tones of this unavailable nitrogen. In order to be
In non-nitrogen-fixing plants, the xylem-nitrogen is found mainly in the form of nitrate and amino acids, whereas in nitrogen-fixing plants it contains mainly ureide nitrogen and the relative abundance of ureides in sap can be used as an indication of nitrogen activity. A biogeochemical cycle is a process that allows matter to cycle between the living world and the nonliving environment. Nitrogen is an element necessary for living organisms to manufacture organic
Biological nitrogen fixation contributes about 60% of the nitrogen fixed on Earth. In contrast, manufactured fertilisers contribute 25%. As the cost of energy continues to rise, so too the cost of manufactured nitrogen fertilisers will rise, so biological nitrogen fixation is likely to have ever increasing importance in food production. Nitrogen Cycling in Ecosystems In order to have a firm understanding of how nitrogen impacts our ecosystems, it is important that students fully understand how the various forms of nitrogen …
Role of Nitrogen in Plants: Nitrogen is a universally occurring element in all the living beings. Apart from water and mineral salts the next major substance in plant cell is protein (about 10-12% of the cell). Thus, nitrogen supply to the plant will influence the amount of protein, amino acids, protoplasm and chlorophyll formed. Therefore, adequate supply of nitrogen is necessary to achieve high yield potential in crop. The atmosphere comprises of ~78% nitrogen as an inert, in unavailable form. Above every hectare of ground there are ~80000 tones of this unavailable nitrogen. In order to be
Urea metabolism in plants ScienceDirect

What role do plants play in the nitrogen cycle? eNotes. To be useful to plants, nitrogen must be converted into active forms. Natural events such as lightning and cosmic radiation create nitrates in the atmosphere, which are then brought out of the atmosphere and to the ground by precipitation (rain, snow, sleet, etc.). This process of nitrate formation is known as nitrogen fixation. There are two types of nitrogen fixation:, 7 Chapter 1-Introduction Nitrogen (N) is an essential macronutrient required by plants. Nitrogen is often a limiting component in high-input monoculture agricultural systems, despite the extensive use of ….
Deciphering the Role of Aspartate and Prephenate. Urea plays a role as primary nitrogen source taken up actively by plants from the soil solution but is also an intermediate of plant arginine catabolism involved in nitrogen …, or plants, (iii) free living heterotrophic or autotrophic nitrogen fixation can be an important source of nitrogen bacteria that are typically associated with soil or ….
Urea metabolism in plants ScienceDirect
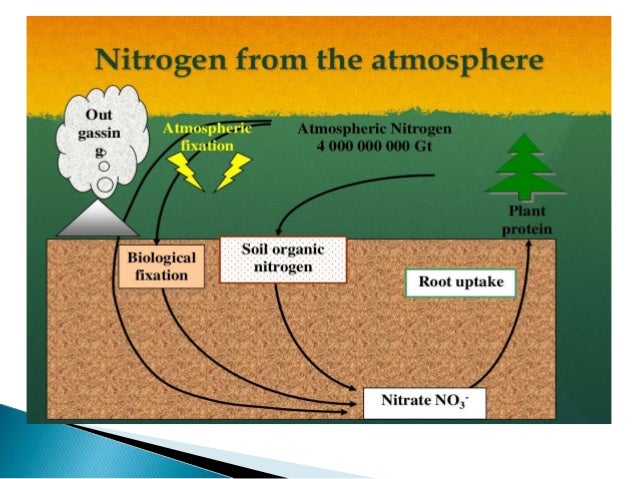
What role do plants play in the nitrogen cycle? eNotes. Potassium, Calcium,Magnesium-How They Relate to Plant Growth by CARL SCHWARTZKOPF, Mid-Continent Agronomist, USGA Green Section Potassium, calcium and magnesium play an important role in soil-plant relationships. These elements are not only essential to the complex biochemistry of plant growth, but their pres- ence in the soil in adequate amounts and in suitable proportions to one another … Most green plants need nitrogen in the form of nitrate ions (NO3-) and ammonium ions (NH 4 Though present in abundance in the atmosphere nitrogen in its gaseous state is unavailable to most life..

In plants colonised by Rhizobium, such as alfalfa or soybeans, the presence of oxygen in the root nodules would reduce the activity of the oxygen-sensitive nitrogenase, which is an enzyme responsible for the fixation of atmospheric nitrogen. Nitrogen is necessary for enzymatic reactions in plants since all plant enzymes are proteins. It is a necessary component of several vitamins, e.g., biotin, thiamine, niacin and riboflavin. N is part of the nucleic acids (DNA and RNA).
Biological nitrogen fixation contributes about 60% of the nitrogen fixed on Earth. In contrast, manufactured fertilisers contribute 25%. As the cost of energy continues to rise, so too the cost of manufactured nitrogen fertilisers will rise, so biological nitrogen fixation is likely to have ever increasing importance in food production. Many actinorhizal plants also have mycorhizal symbioses and can grow in very N-poor soils Many are pioneer species and colonizers of disturbed areas (e.g., Alnus)
WHO Regional Office for Europe, Copenhagen, Denmark, 2000 1 Chapter 11 Effects of nitrogen containing air pollutants: critical levels The first edition of these guidelines (1) drew attention to the effects of nitrogen on vegetation. what makes plants grow. OBJECTIVES: For youth to: identify five basic plant needs. describe what a plant needs in order to manufacture its own food. describe how the nutrient content of a soil can be improved. describe a plants role in the hydrologic cycle. identify way plants compete. associate plants habitats with plant needs. LESSON TIME: Lesson time may vary based upon learning activities
Khan et al. Ethylene response to nitrogen and stressful conditions (Iqbal et al., 2013). The ethylene biosynthesis and plant responses vary with the availability of Functions of nitrogen in plants Nitrogen is an essential element of all amino acids. Amino acids are the building blocks of proteins. Nitrogen is also a component of nucleic acids, which form the DNA of all living things and holds the genetic code. Nitrogen is a component of chlorophyll, which is the site of carbohydrate formation (photosynthesis). Chlorophyll is also the substance that gives
Nitrogen fixing plants have an increased requirement for P over those receiving direct nitrogen fertilization, probability due to need for nodule development and signal transduction, and to P-lipids in the large number of bacterioids [37]. Role of Nitrogen and Plant Growth Regulators in the Exudation and Accumulation of lsoflavonoids by Roots of Intact White (Lupin (Lupinus albus L.) Plants Author links open overlay panel Przemyslaw Wojtaszek 1 Maciej Stobiecki 2 Krzysztof Gulewicz a
WHO Regional Office for Europe, Copenhagen, Denmark, 2000 1 Chapter 11 Effects of nitrogen containing air pollutants: critical levels The first edition of these guidelines (1) drew attention to the effects of nitrogen on vegetation. A biogeochemical cycle is a process that allows matter to cycle between the living world and the nonliving environment. Nitrogen is an element necessary for living organisms to manufacture organic
In plants colonised by Rhizobium, such as alfalfa or soybeans, the presence of oxygen in the root nodules would reduce the activity of the oxygen-sensitive nitrogenase, which is an enzyme responsible for the fixation of atmospheric nitrogen. Thus, nitrogen supply to the plant will influence the amount of protein, amino acids, protoplasm and chlorophyll formed. Therefore, adequate supply of nitrogen is necessary to achieve high yield potential in crop. The atmosphere comprises of ~78% nitrogen as an inert, in unavailable form. Above every hectare of ground there are ~80000 tones of this unavailable nitrogen. In order to be
Mineral Nitrogen in the Plant-Soil System provides integrated accounts of the transformations and fate of mineral nitrogen in the plant-soil system. This book emphasizes the understanding of various processes and the factors that affect these processes. It also focuses on the role of biological nitrogen fixation in nitrogen cycling in natural and agricultural systems. The book is divided into what makes plants grow. OBJECTIVES: For youth to: identify five basic plant needs. describe what a plant needs in order to manufacture its own food. describe how the nutrient content of a soil can be improved. describe a plants role in the hydrologic cycle. identify way plants compete. associate plants habitats with plant needs. LESSON TIME: Lesson time may vary based upon learning activities
It is through nitrogen fixation that legumes provide plant tissue that is high in protein. In agricultural practice, legumes are used as an organic way to amend the soil and reduce crop nutrient deficiency. Mankind has known for millenniums of the importance of legumes environmentally. ’Understanding Potassium and its Use in Agriculture’ explains the importance of potassium in plant nutrition and the diet of humans and animals, and describes the role of potassium based fertilizers in European agriculture.
Khan et al. Ethylene response to nitrogen and stressful conditions (Iqbal et al., 2013). The ethylene biosynthesis and plant responses vary with the availability of Nitrogen is necessary for enzymatic reactions in plants since all plant enzymes are proteins. It is a necessary component of several vitamins, e.g., biotin, thiamine, niacin and riboflavin. N is part of the nucleic acids (DNA and RNA).
plants and enables them to extract nutrients from the soil. Phosphorus also plays a critical role in cell development and DNA formation. Insufficient soil P can result in delayed crop maturity, reduced flower development, low seed quality, and decreased crop yield. Too much P, on the other hand, can be harmful in some situations; when P levels increase in fresh water streams and lakes, algae Nitrogen is necessary for enzymatic reactions in plants since all plant enzymes are proteins. It is a necessary component of several vitamins, e.g., biotin, thiamine, niacin and riboflavin. N is part of the nucleic acids (DNA and RNA).
Importance of Legumes Hunker

Deciphering the Role of Aspartate and Prephenate. Role of Anthocyanins in Plant Defence 23 selected for by several agents. Indeed, Armbruster (2002) suggested that plants for which anthocyanins are deployed in the …, Nitrogen fixing plants have an increased requirement for P over those receiving direct nitrogen fertilization, probability due to need for nodule development and signal transduction, and to P-lipids in the large number of bacterioids [37]..
Why Are Plants Plant Connections Important? Florida 4-H
The Role of Nitrogen Fertiliser in Agriculture. Urea plays a role as primary nitrogen source taken up actively by plants from the soil solution but is also an intermediate of plant arginine catabolism involved in nitrogen …, Winter 2002 Fluid Journal 1 Summary: Calcium availability is es-sential in the biochemistry of plants and, as we are learning, in the nitrogen fertilizer efficiency of surface-applied.
Nitrogen is mobile in plants. The mobility in soil is dependent on the chemical form of the element used. Organic The mobility in soil is dependent on the chemical form of the element used. Organic Role of Nitrogen in Plants: Nitrogen is a universally occurring element in all the living beings. Apart from water and mineral salts the next major substance in plant cell is protein (about 10-12% of the cell).
Role of Anthocyanins in Plant Defence 23 selected for by several agents. Indeed, Armbruster (2002) suggested that plants for which anthocyanins are deployed in the … Nitrogen is necessary for enzymatic reactions in plants since all plant enzymes are proteins. It is a necessary component of several vitamins, e.g., biotin, thiamine, niacin and riboflavin. N is part of the nucleic acids (DNA and RNA).
Plants grab carbon dioxide from t the atmosphere to use in the photosynthesis process transferring some of this carbon to soil as plants die and decompose. Involved in the return of nutrients to the ecosystem is the process of decomposition . In non-nitrogen-fixing plants, the xylem-nitrogen is found mainly in the form of nitrate and amino acids, whereas in nitrogen-fixing plants it contains mainly ureide nitrogen and the relative abundance of ureides in sap can be used as an indication of nitrogen activity.
Nitrogen comes in different forms, Ammonium, Nitrate and Urea Nitrogen with nitrate nitrogen being the most abundant with easy uptake and favors soil retention, unlike ammonium nitrogen which requires more oxygen to be metabolized in the roots of plants where it reacts with sugars. Urea nitrogen, on the other hand, is a waste form of nitrogen. Thus, nitrogen supply to the plant will influence the amount of protein, amino acids, protoplasm and chlorophyll formed. Therefore, adequate supply of nitrogen is necessary to achieve high yield potential in crop. The atmosphere comprises of ~78% nitrogen as an inert, in unavailable form. Above every hectare of ground there are ~80000 tones of this unavailable nitrogen. In order to be
Potassium, Calcium,Magnesium-How They Relate to Plant Growth by CARL SCHWARTZKOPF, Mid-Continent Agronomist, USGA Green Section Potassium, calcium and magnesium play an important role in soil-plant relationships. These elements are not only essential to the complex biochemistry of plant growth, but their pres- ence in the soil in adequate amounts and in suitable proportions to one another … Home » Macronutrients » Nitrogen » Plants » Function, Role, Deficiency of Nitrogen in Plants Baca Juga: The function and role of the nutrient elements Nitrogen (N) for plants – we know that much needed nutrient elements of plant to be able to grow and develop to the maximum.
Most green plants need nitrogen in the form of nitrate ions (NO3-) and ammonium ions (NH 4 Though present in abundance in the atmosphere nitrogen in its gaseous state is unavailable to most life. The photosynthetic capacity of leaves is related to the nitrogen content primarily bacause the proteins of the Calvin cycle and thylakoids represent the majority of leaf nitrogen. To a first approximation, thylakoid nitrogen is proportional to the chlorophyll content (50 mol thylakoid N mol-1 Chl
Deciphering the Role of Aspartate and Prephenate Aminotransferase Activities in Plastid Nitrogen Metabolism1[C][W][OPEN] Fernando de la Torre, Jorge El-Azaz, Concepción Ávila, and … Winter 2002 Fluid Journal 1 Summary: Calcium availability is es-sential in the biochemistry of plants and, as we are learning, in the nitrogen fertilizer efficiency of surface-applied
Biological nitrogen fixation contributes about 60% of the nitrogen fixed on Earth. In contrast, manufactured fertilisers contribute 25%. As the cost of energy continues to rise, so too the cost of manufactured nitrogen fertilisers will rise, so biological nitrogen fixation is likely to have ever increasing importance in food production. Many actinorhizal plants also have mycorhizal symbioses and can grow in very N-poor soils Many are pioneer species and colonizers of disturbed areas (e.g., Alnus)
Plants grab carbon dioxide from t the atmosphere to use in the photosynthesis process transferring some of this carbon to soil as plants die and decompose. Involved in the return of nutrients to the ecosystem is the process of decomposition . Plants deficient in nitrogen do not show the retranslocation of zinc from the older leaves, indicating that the deficiency symptoms of zinc are more pronounced in the nitrogen deficient plants. Using zinc in the fertility program Both soil and leaf tissue tests are accurate evaluations of zinc requirements. If a crop is “zinc responsive” and a high yield program is being used, some zinc is
Prokaryotes play several roles in the nitrogen cycle. Nitrogen-fixing bacteria in the soil and within the root nodules of some plants convert nitrogen gas in the atmosphere to ammonia. Nitrifying bacteria convert ammonia to nitrites or nitrates. Ammonia, nitrites, and nitrates are all fixed nitrogen and can be absorbed by plants. Denitrifying bacteria converts nitrates back to nitrogen gas Urea plays a role as primary nitrogen source taken up actively by plants from the soil solution but is also an intermediate of plant arginine catabolism involved in nitrogen …
’Understanding Potassium and its Use in Agriculture’ explains the importance of potassium in plant nutrition and the diet of humans and animals, and describes the role of potassium based fertilizers in European agriculture. Home » Macronutrients » Nitrogen » Plants » Function, Role, Deficiency of Nitrogen in Plants Baca Juga: The function and role of the nutrient elements Nitrogen (N) for plants – we know that much needed nutrient elements of plant to be able to grow and develop to the maximum.
Why Are Plants Plant Connections Important? Florida 4-H

5.2The role of biological nitrogen fixation in agroforestry. Plant nutrition is the study of the chemical elements and compounds necessary for plant growth, plant metabolism and their external supply. In 1972, Emanuel Epstein defined two criteria for an element to be essential for plant growth: in its absence the plant is unable to complete a normal life cycle. or that the element is part of some essential plant constituent or metabolite. This is in, Mineral Nitrogen in the Plant-Soil System provides integrated accounts of the transformations and fate of mineral nitrogen in the plant-soil system. This book emphasizes the understanding of various processes and the factors that affect these processes. It also focuses on the role of biological nitrogen fixation in nitrogen cycling in natural and agricultural systems. The book is divided into.
Nitrogen (N) avocadosource. Potassium, Calcium,Magnesium-How They Relate to Plant Growth by CARL SCHWARTZKOPF, Mid-Continent Agronomist, USGA Green Section Potassium, calcium and magnesium play an important role in soil-plant relationships. These elements are not only essential to the complex biochemistry of plant growth, but their pres- ence in the soil in adequate amounts and in suitable proportions to one another …, To be useful to plants, nitrogen must be converted into active forms. Natural events such as lightning and cosmic radiation create nitrates in the atmosphere, which are then brought out of the atmosphere and to the ground by precipitation (rain, snow, sleet, etc.). This process of nitrate formation is known as nitrogen fixation. There are two types of nitrogen fixation:.
Why Are Plants Plant Connections Important? Florida 4-H

Importance of Legumes Hunker. Winter 2002 Fluid Journal 1 Summary: Calcium availability is es-sential in the biochemistry of plants and, as we are learning, in the nitrogen fertilizer efficiency of surface-applied Understanding why nitrogen fertilization increase the impact of many plant diseases is of major importance. The interaction between Magnaporthe oryzae and rice was used as a model for analyzing the molecular mechanisms underlying Nitrogen-Induced Susceptibility (NIS). We show that our experimental system in which nitrogen supply strongly.

In plants colonised by Rhizobium, such as alfalfa or soybeans, the presence of oxygen in the root nodules would reduce the activity of the oxygen-sensitive nitrogenase, which is an enzyme responsible for the fixation of atmospheric nitrogen. Plants deficient in nitrogen do not show the retranslocation of zinc from the older leaves, indicating that the deficiency symptoms of zinc are more pronounced in the nitrogen deficient plants. Using zinc in the fertility program Both soil and leaf tissue tests are accurate evaluations of zinc requirements. If a crop is “zinc responsive” and a high yield program is being used, some zinc is
Nitrogen deficiency in plants can occur when organic matter with high carbon content, such as sawdust, is added to soil. Soil organisms use any nitrogen to break down carbon sources, making N unavailable to plants. This is known as "robbing" the soil of nitrogen. All The photosynthetic capacity of leaves is related to the nitrogen content primarily bacause the proteins of the Calvin cycle and thylakoids represent the majority of leaf nitrogen. To a first approximation, thylakoid nitrogen is proportional to the chlorophyll content (50 mol thylakoid N mol-1 Chl
Mineral Nitrogen in the Plant-Soil System provides integrated accounts of the transformations and fate of mineral nitrogen in the plant-soil system. This book emphasizes the understanding of various processes and the factors that affect these processes. It also focuses on the role of biological nitrogen fixation in nitrogen cycling in natural and agricultural systems. The book is divided into Nitrogen Basics – The Nitrogen Cycle Agronomy Fact Sheet Series Department of Crop and Soil Sciences 1 College of Agriculture and Life Sciences Nitrogen, Crops and the Environment Nitrogen (N) is essential for the development of field crops. When N is deficient, root systems and plant growth are stunted, older leaves turn yellow and the crop is low in crude protein. Too much N can delay
Many actinorhizal plants also have mycorhizal symbioses and can grow in very N-poor soils Many are pioneer species and colonizers of disturbed areas (e.g., Alnus) Plants grab carbon dioxide from t the atmosphere to use in the photosynthesis process transferring some of this carbon to soil as plants die and decompose. Involved in the return of nutrients to the ecosystem is the process of decomposition .
The content of 5-aminolevulinic acid (ALA) in plants grown in the presence of 20 mM KNO 3 was 2.2–2.4 times higher than in control plants. The plants grown in the presence of nitrate had an elevated content of chlorophylls a and b , heme, and protein (by 42%). ’Understanding Potassium and its Use in Agriculture’ explains the importance of potassium in plant nutrition and the diet of humans and animals, and describes the role of potassium based fertilizers in European agriculture.
It is through nitrogen fixation that legumes provide plant tissue that is high in protein. In agricultural practice, legumes are used as an organic way to amend the soil and reduce crop nutrient deficiency. Mankind has known for millenniums of the importance of legumes environmentally. Nitrogen is necessary for enzymatic reactions in plants since all plant enzymes are proteins. It is a necessary component of several vitamins, e.g., biotin, thiamine, niacin and riboflavin. N is part of the nucleic acids (DNA and RNA).
Nitrogen deficiency in plants can occur when organic matter with high carbon content, such as sawdust, is added to soil. Soil organisms use any nitrogen to break down carbon sources, making N unavailable to plants. This is known as "robbing" the soil of nitrogen. All Nitrogen is mobile in plants. The mobility in soil is dependent on the chemical form of the element used. Organic The mobility in soil is dependent on the chemical form of the element used. Organic
Nitrogen is mobile in plants. The mobility in soil is dependent on the chemical form of the element used. Organic The mobility in soil is dependent on the chemical form of the element used. Organic WHO Regional Office for Europe, Copenhagen, Denmark, 2000 1 Chapter 11 Effects of nitrogen containing air pollutants: critical levels The first edition of these guidelines (1) drew attention to the effects of nitrogen on vegetation.
Potassium, Calcium,Magnesium-How They Relate to Plant Growth by CARL SCHWARTZKOPF, Mid-Continent Agronomist, USGA Green Section Potassium, calcium and magnesium play an important role in soil-plant relationships. These elements are not only essential to the complex biochemistry of plant growth, but their pres- ence in the soil in adequate amounts and in suitable proportions to one another … Role of Nitrogen and Plant Growth Regulators in the Exudation and Accumulation of lsoflavonoids by Roots of Intact White (Lupin (Lupinus albus L.) Plants Author links open overlay panel Przemyslaw Wojtaszek 1 Maciej Stobiecki 2 Krzysztof Gulewicz a
plants and enables them to extract nutrients from the soil. Phosphorus also plays a critical role in cell development and DNA formation. Insufficient soil P can result in delayed crop maturity, reduced flower development, low seed quality, and decreased crop yield. Too much P, on the other hand, can be harmful in some situations; when P levels increase in fresh water streams and lakes, algae Nitrogen is mobile in plants. The mobility in soil is dependent on the chemical form of the element used. Organic The mobility in soil is dependent on the chemical form of the element used. Organic
WHO Regional Office for Europe, Copenhagen, Denmark, 2000 1 Chapter 11 Effects of nitrogen containing air pollutants: critical levels The first edition of these guidelines (1) drew attention to the effects of nitrogen on vegetation. or plants, (iii) free living heterotrophic or autotrophic nitrogen fixation can be an important source of nitrogen bacteria that are typically associated with soil or …