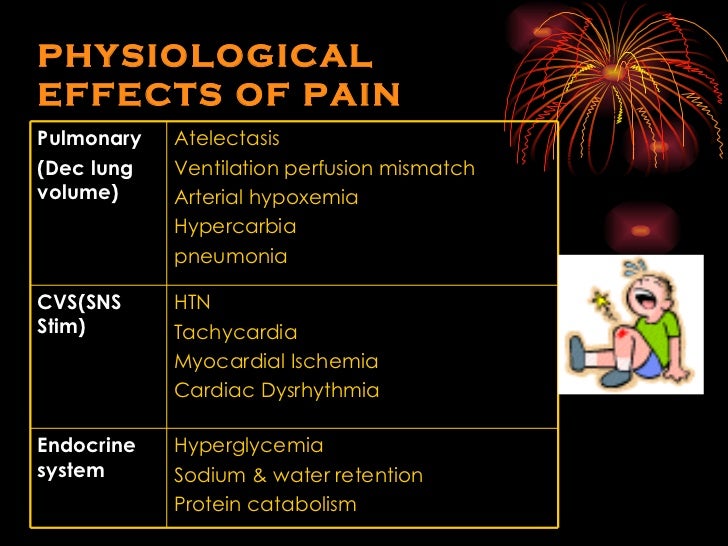
Why is sodium important for human survival? Modern Ghana • Sodium is an essential nutrient and is needed by the human body in occur). • Sodium is important for many body processes, such as fluid balance, muscle contraction, and nervous system function. • As a food ingredient, sodium has multiple uses, such as for curing meat, baking, thickening, retaining moisture, enhancing flavor (including the flavor of other ingredients), and as a
Sodium and human physiology SLU.SE
FOOD SCIENCE AND HUMAN NUTRITION Role of Sodium in. Role of Sodium in Human Body The human body contains approximately 1.3 g of sodium. About a third is found in our bones. The rest is our body fluids. It ensures a proper fluid and electrolyte or pH balance in our body, together with chlorine and potassium. Sodium in the form of sodium chloride is ingested directly though food and many food materials contain this material. Sodium helps our body, Chloride is one of the major minerals in the human body and helps fluid levels in the body remain balanced by working closely with both sodium and potassium. Chloride works by maintaining fluid levels on the outside of cells in the body. Chloride is also an important contributor to the making of.
The body maintains the right level of potassium by matching the amount of potassium consumed with the amount lost. Potassium is consumed in food and drinks that contain electrolytes (including potassium) and lost primarily in urine. Sodium performs an important function in the human body.. It is responsible for the blood pressure of our body.. High or low blood pressure can cause unnecessary problems for us.. Sodium also helps the nerves and the muscles to function properly.
Calcium has many roles in the human body. 99% of our calcium is used for building bones. Our bones are made of hydroapatite, a calsium phosphate matrix that is both stable and easy to restructure. Sodium is a chemical element with symbol Na (from Latin natrium) and atomic number 11. It is a soft, silvery-white, highly reactive metal. Sodium is an alkali metal, being in group 1 of the periodic table, because it has a single electron in its outer shell that it readily donates, creating a positively charged ion—the Na + cation.
The human body has an elaborate system for managing and regulating the amount of key trace metals circulating in blood and stored in cells. Nutrient metals from our diet are incorporated into blood if blood levels are depleted, transported into cells if cellular levels are inadequate, or excreted if blood and cell levels are sufficient or overloaded. When this system fails to function properly Sodium is a chemical element with symbol Na (from Latin natrium) and atomic number 11. It is a soft, silvery-white, highly reactive metal. Sodium is an alkali metal, being in group 1 of the periodic table, because it has a single electron in its outer shell that it readily donates, creating a positively charged ion—the Na + cation.
Sodium is a mineral element which is an important part of the human body. It controls the volume of fluid in the body and helps maintain the acid-base level. About 40% of the body’s sodium is contained in bone, some is found within organs and cells and the remaining 55% is in blood plasma and other fluids outside cells. Sodium is important in proper nerve conduction, the passage of various A sodium deficiency is a health condition where a body fails to receive an adequate supply of sodium. Sodium deficiency can become extremely prevalent in excessive temperatures, which cause the body to perspire heavily and patterns of dehydration will set in. Sodium deficiency can lead to shock if the blood pressure is decreased too severely. Salt is important to good nutritional status. Too
Sodium and potassium are two important elements that play a vital role in the metabolic processes in the human body. Maintaining the ratio between these two elements is key to good health. The human species evolved in the warm climate of Africa, a salt-poor continent, on a low-salt diet (as low as 50 mg sodium per day). Humans have come to depend on the physiological retention of the limited salt naturally present in food (Elliot and Brown, 2006).
The body maintains the right level of potassium by matching the amount of potassium consumed with the amount lost. Potassium is consumed in food and drinks that contain electrolytes (including potassium) and lost primarily in urine. Potassium is a mineral necessary for the proper function of many of your body systems; it's also often referred to as one of the key electrolytes in your body. Potassium, along with sodium, the other electrolyte, plays a vital role in regulating the fluid levels in your body. Potassium has many
A sodium deficiency is a health condition where a body fails to receive an adequate supply of sodium. Sodium deficiency can become extremely prevalent in excessive temperatures, which cause the body to perspire heavily and patterns of dehydration will set in. Sodium deficiency can lead to shock if the blood pressure is decreased too severely. Salt is important to good nutritional status. Too There are hundreds of sulfur-containing compounds in the human body, and the body synthesizes all of them, with the exception of the vitamins thiamin and biotin. Precursors include sulfate obtained from dietary intake and ingestion of the indispensable amino acids methionine and cysteine (cysteine is considered conditionally indispensable) (Shils et al., 1999). One of the important roles for
Sodium is a mineral element which is an important part of the human body. It controls the volume of fluid in the body and helps maintain the acid-base level. About 40% of the body’s sodium is contained in bone, some is found within organs and cells and the remaining 55% is in blood plasma and other fluids outside cells. Sodium is important in proper nerve conduction, the passage of various Sodium helps the body keep fluids in a normal balance (see About Body Water). Sodium plays a key role in normal nerve and muscle function. Sodium plays a key role in normal nerve and muscle function. The body obtains sodium through food and drink and loses it primarily in sweat and urine.
Potassium is one of the major electrolytes (together with sodium, chloride and magnesium) that conducts electricity in the human body. It also plays important roles in muscle contraction, nerve impulse transmission, and in maintaining the balance of fluids in the body. Role of Sodium And Potassium in conduction: Water in its pure form does not possess the capability to conduct electricity. Sodium and potassium ions along with other electrolytes present in the body are responsible for the conduction of electricity through water.
Potassium is one of the major electrolytes (together with sodium, chloride and magnesium) that conducts electricity in the human body. It also plays important roles in muscle contraction, nerve impulse transmission, and in maintaining the balance of fluids in the body. • Sodium is important for many body processes, such as fluid balance, muscle contraction, and nervous system function. • As a food ingredient, sodium has multiple uses, such as for curing meat,
Salt & the Function of Our Cells The Salt Association

Hyponatremia (Low Level of Sodium in the Blood) Hormonal. Importance of Sodium in the Human Body. Sodium is a mineral used by the body for purposes of controlling blood pressure. It is defined as an electrolyte controlling extracellular body fluids., Chloride plays a critical role in keeping the proper balance of body fluids and maintaining the body's acid-base balance. The normal chloride values are 96 to 106 mEq/L. The normal chloride values are 96 ….
Electrolytes Sodium Potassium Chloride MedicineNet. The effects of sodium in the human body include maintaining electrolyte balance in the bloodstream and the proper working of the nervous and muscular systems. HealthCentral says that sodium is an important determinant of the volume of blood in the body and is an important factor in determining blood, How Much Sodium Should Someone Have in a Day? According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, the human body needs only 180 to 500 milligrams of sodium per day to maintain its healthy function..
THE HORMONAL CONTROL OF BODY SODIUM pmj.bmj.com

The Importance of Salt in Your Diet / Nutrition / Healthy. The sodium-potassium pump is a vital enzyme found in all human cells which constantly maintains an optimal ion balance. This uses up a great deal of energy - about a fourth of the body's energy • Sodium is an essential nutrient and is needed by the human body in occur). • Sodium is important for many body processes, such as fluid balance, muscle contraction, and nervous system function. • As a food ingredient, sodium has multiple uses, such as for curing meat, baking, thickening, retaining moisture, enhancing flavor (including the flavor of other ingredients), and as a.

Based on the entire body of evidence, WHO generated the following recommendations for sodium intake in adults and children. • WHOecommends r a reduction in sodium … A sodium deficiency is a health condition where a body fails to receive an adequate supply of sodium. Sodium deficiency can become extremely prevalent in excessive temperatures, which cause the body to perspire heavily and patterns of dehydration will set in. Sodium deficiency can lead to shock if the blood pressure is decreased too severely. Salt is important to good nutritional status. Too
Based on the entire body of evidence, WHO generated the following recommendations for sodium intake in adults and children. • WHOecommends r a reduction in sodium … Electrolytes are vital for the normal functioning of the human body. Fruits and vegetables are good sources of electrolytes. Common electrolytes include sodium, potassium , calcium and bicarbonate.
Sodium is a mineral element which is an important part of the human body. It controls the volume of fluid in the body and helps maintain the acid-base level. About 40% of the body’s sodium is contained in bone, some is found within organs and cells and the remaining 55% is in blood plasma and other fluids outside cells. Sodium is important in proper nerve conduction, the passage of various The Role of Calcium in the Human Body Calcium is a mineral necessary to build and maintain strong bones and teeth, which also aids a number of other body processes. These include blood clotting, blood vessel and muscle contraction, enzyme and hormone secretion and …
Role of Sodium in Human Body The human body contains approximately 1.3 g of sodium. About a third is found in our bones. The rest is our body fluids. It ensures a proper fluid and electrolyte or pH balance in our body, together with chlorine and potassium. Sodium in the form of sodium chloride is ingested directly though food and many food materials contain this material. Sodium helps our body Sodium • The body needs a small amount of sodium to help maintain normal blood pressure and normal function of muscles and nerves. • Sodium is found in table salt, baking soda, monosodium glutamate (MSG), various seasonings, additives, condiments, meat, fish, poultry, dairy foods, eggs, smoked meats, olives, and pickled foods.
Sodium performs an important function in the human body.. It is responsible for the blood pressure of our body.. High or low blood pressure can cause unnecessary problems for us.. Sodium also helps the nerves and the muscles to function properly. The body maintains the right level of potassium by matching the amount of potassium consumed with the amount lost. Potassium is consumed in food and drinks that contain electrolytes (including potassium) and lost primarily in urine.
Sodium is a nutrient that is ubiquitous in the food supply and plays an essential role in human physiology. Excess sodium intakes have been associated with increased chronic disease risk, and in particular high blood pressure ( NHMRC 2013). Like sodium, chlorine is also very important for the proper functioning of the human body. There is no There is no richer source of chlorine in our diet than the “chloride” found in sodium chloride.
A sodium deficiency is a health condition where a body fails to receive an adequate supply of sodium. Sodium deficiency can become extremely prevalent in excessive temperatures, which cause the body to perspire heavily and patterns of dehydration will set in. Sodium deficiency can lead to shock if the blood pressure is decreased too severely. Salt is important to good nutritional status. Too Sodium is a chemical element with symbol Na (from Latin natrium) and atomic number 11. It is a soft, silvery-white, highly reactive metal. Sodium is an alkali metal, being in group 1 of the periodic table, because it has a single electron in its outer shell that it readily donates, creating a positively charged ion—the Na + cation.
• Sodium is important for many body processes, such as fluid balance, muscle contraction, and nervous system function. • As a food ingredient, sodium has multiple uses, such as for curing meat, Sodium and potassium are two important elements that play a vital role in the metabolic processes in the human body. Maintaining the ratio between these two elements is key to good health.
Sodium is commonly available from common salt or sodium chloride. About 50% of the total sodium present in the human body is found in the extracellular fluids- the fluids within the blood vessels. The remaining amount is distributed in the blood, blood plasma and intracellular fluids. Sodium can be Iodine is a vital micronutrient required at all stages of life; fetal life and early childhood being the most critical phases of requirement. Diet is the sole source of iodine, which in turn is dependent upon the iodine content of water and soil. Iodine is metabolized in the human body through a
The most important extracellular anion in the human body, chloride serves many bodily functions, including maintenance of osmotic pressure, acid–base balance, and muscular activity and movement of water between fluid compartments . Chloride channels are evolutionarily conserved across eukaryotes, confirming their primacy in the most essential of cellular functions. A broad spectrum of The body maintains the right level of potassium by matching the amount of potassium consumed with the amount lost. Potassium is consumed in food and drinks that contain electrolytes (including potassium) and lost primarily in urine.

Sodium plays a key role in normal nerve and muscle function. The body obtains sodium through food and drink and loses it primarily in sweat and urine. Healthy kidneys maintain a consistent level of sodium in the body by adjusting the amount excreted in the urine. Sodium performs an important function in the human body.. It is responsible for the blood pressure of our body.. High or low blood pressure can cause unnecessary problems for us.. Sodium also helps the nerves and the muscles to function properly.
Electrolytes Sodium Potassium Chloride MedicineNet

Organic Uses Of Sodium And Potassium Chemistry. Bicarbonate is present in all body fluids (see table) and organs and plays a major role in the acid-base balances in the human body. The first organ where food, beverages and water stay in our body is the stomach. The mucus membrane of the human stomach has 30 million glands which produce gastric juice containing not only acids, but also bicarbonate. The flow of bicarbonate in the stomach, The sodium-potassium pump is a vital enzyme found in all human cells which constantly maintains an optimal ion balance. This uses up a great deal of energy - about a fourth of the body's energy.
Overview of Phosphate's Role in the Body Hormonal and
Sodium Levels & Sodium Blood Test WebMD. Iodine is a vital micronutrient required at all stages of life; fetal life and early childhood being the most critical phases of requirement. Diet is the sole source of iodine, which in turn is dependent upon the iodine content of water and soil. Iodine is metabolized in the human body through a, 7/02/2007В В· Best Answer: Sodium has many functions in the body. It helps regulate intracellular fluid levels, is the chief extracellular electrolyte, is involved in electrical transmission and involved in muscular contraction..
There are hundreds of sulfur-containing compounds in the human body, and the body synthesizes all of them, with the exception of the vitamins thiamin and biotin. Precursors include sulfate obtained from dietary intake and ingestion of the indispensable amino acids methionine and cysteine (cysteine is considered conditionally indispensable) (Shils et al., 1999). One of the important roles for The body precisely controls the amount of calcium in cells and blood. The body moves calcium out of bones into blood as needed to maintain a steady level of calcium in the blood. If people do not consume enough calcium , too much calcium is mobilized from the bones, weakening them.
Sodium is commonly available from common salt or sodium chloride. About 50% of the total sodium present in the human body is found in the extracellular fluids- the fluids within the blood vessels. The remaining amount is distributed in the blood, blood plasma and intracellular fluids. Sodium can be • Sodium is an essential nutrient and is needed by the human body in occur). • Sodium is important for many body processes, such as fluid balance, muscle contraction, and nervous system function. • As a food ingredient, sodium has multiple uses, such as for curing meat, baking, thickening, retaining moisture, enhancing flavor (including the flavor of other ingredients), and as a
The human species evolved in the warm climate of Africa, a salt-poor continent, on a low-salt diet (as low as 50 mg sodium per day). Humans have come to depend on the physiological retention of the limited salt naturally present in food (Elliot and Brown, 2006). How Much Sodium Should Someone Have in a Day? According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, the human body needs only 180 to 500 milligrams of sodium per day to maintain its healthy function.
The Role of Calcium in the Human Body Calcium is a mineral necessary to build and maintain strong bones and teeth, which also aids a number of other body processes. These include blood clotting, blood vessel and muscle contraction, enzyme and hormone secretion and … Sodium is commonly available from common salt or sodium chloride. About 50% of the total sodium present in the human body is found in the extracellular fluids- the fluids within the blood vessels. The remaining amount is distributed in the blood, blood plasma and intracellular fluids. Sodium can be
Sodium and potassium are essential for the body’s electrical system. A 170 pound person has around 5 oz of sodium and 10 oz of potassium in their body. The electrical system not only keeps our heart beating but also provides the energy for nerve signals and muscle contractions. Potassium is one of the major electrolytes (together with sodium, chloride and magnesium) that conducts electricity in the human body. It also plays important roles in muscle contraction, nerve impulse transmission, and in maintaining the balance of fluids in the body.
The Role of Calcium in the Human Body Calcium is a mineral necessary to build and maintain strong bones and teeth, which also aids a number of other body processes. These include blood clotting, blood vessel and muscle contraction, enzyme and hormone secretion and … Sodium plays a key role in normal nerve and muscle function. The body obtains sodium through food and drink and loses it primarily in sweat and urine. Healthy kidneys maintain a consistent level of sodium in the body by adjusting the amount excreted in the urine.
Potassium is a mineral necessary for the proper function of many of your body systems; it's also often referred to as one of the key electrolytes in your body. Potassium, along with sodium, the other electrolyte, plays a vital role in regulating the fluid levels in your body. Potassium has many HEER, M. Sodium regulation in the human body. Curr. Sports Med. Rep., Vol. 7, No. 4, pp. S3-S6, 2008. The conventional wisdom regarding sodium regulation is that sodium is absorbed fully in the
The Role of Calcium in the Human Body Calcium is a mineral necessary to build and maintain strong bones and teeth, which also aids a number of other body processes. These include blood clotting, blood vessel and muscle contraction, enzyme and hormone secretion and … Like sodium, chlorine is also very important for the proper functioning of the human body. There is no There is no richer source of chlorine in our diet than the “chloride” found in sodium chloride.
Bicarbonate is present in all body fluids (see table) and organs and plays a major role in the acid-base balances in the human body. The first organ where food, beverages and water stay in our body is the stomach. The mucus membrane of the human stomach has 30 million glands which produce gastric juice containing not only acids, but also bicarbonate. The flow of bicarbonate in the stomach Calcium has many roles in the human body. 99% of our calcium is used for building bones. Our bones are made of hydroapatite, a calsium phosphate matrix that is both stable and easy to restructure.
Total Body Water is primarily maintained via extracellular Sodium concentration. Extracellular Sodium is maintained at 135-145 mEq/L; Sodium (Na+) is the … Physiological role of Sodium human body (maintaining acid-base homeostasis). • 70 to 75 percent of CO. 2. in the body is converted into carbonic acid (H. 2. CO. 3), which can quickly turn into bicarbonate (HCO . 3 −). • With carbonic acid as the central intermediate species, bicarbonate – in conjunction with water, hydrogen ions,andcarbon dioxide – forms this buffering system
Dietary Reference Intakes for Water Potassium Sodium
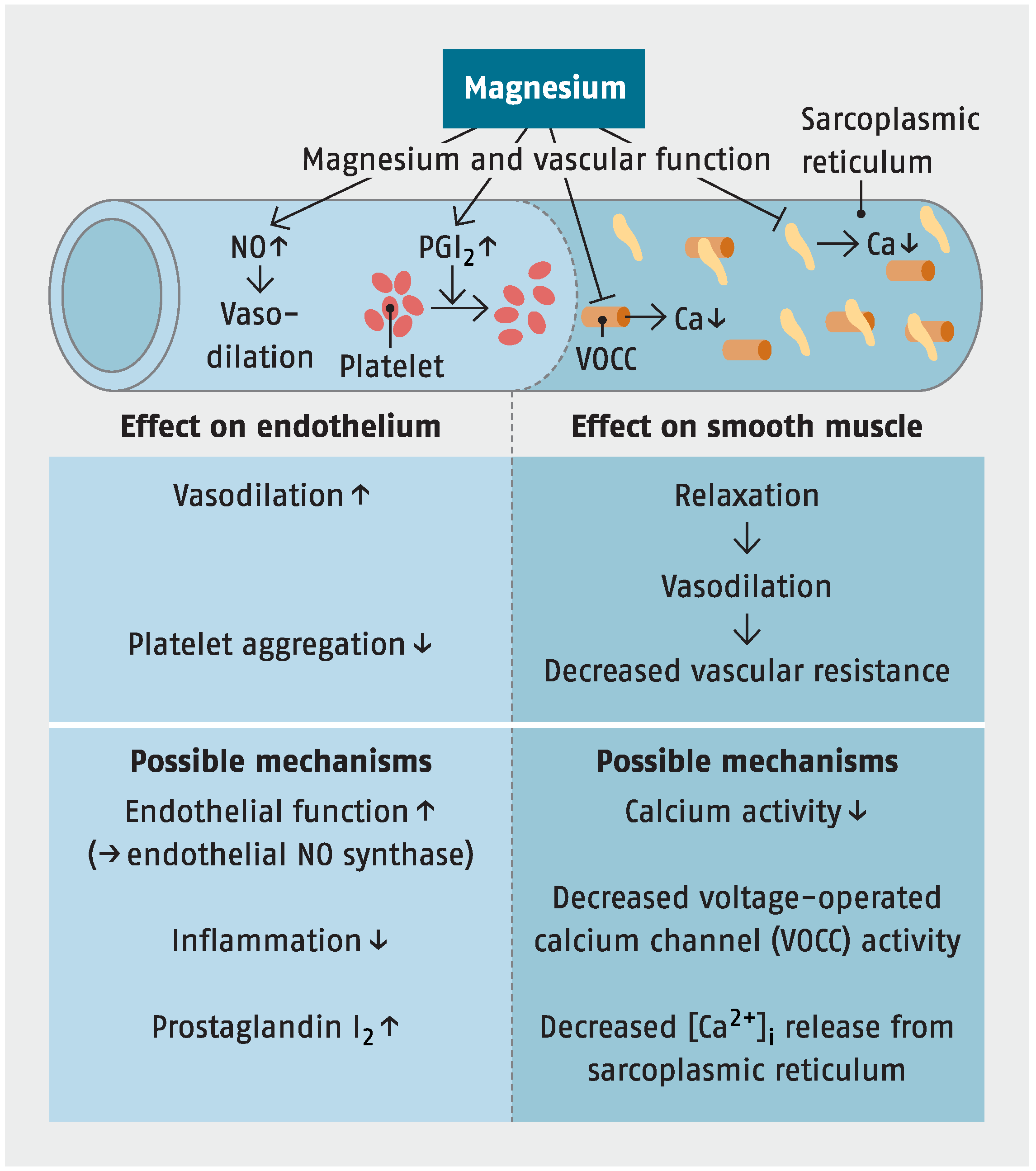
Sodium Function in Human Body IYTmed.com. Hyponatremia occurs when the body contains too little sodium for the amount of fluid it contains. The body may have too much, too little, or a normal amount of fluid. In all cases, however, sodium is diluted. For example, people with severe vomiting or diarrhea lose sodium. If they replace their fluid losses with just water, sodium is diluted., Sodium is an extremely important electrolyte and an essential ion present in the extracellular fluid (ECF). One of the health benefits of sodium is the pivotal role it plays in enzyme operations and muscle contraction. It is very important for osmoregulation and fluid maintenance within the human.
Iodine—A Potential Antioxidant and the Role of Iodine

The Role of Sodium and Chloride in Heart Failure JACC. The body uses sodium to control blood pressure and blood volume. Your body also needs sodium for your muscles and nerves to work properly. Sodium occurs naturally in most foods. The most common form of sodium is sodium chloride, which is table salt. Milk, beets, and celery also naturally contain The body precisely controls the amount of calcium in cells and blood. The body moves calcium out of bones into blood as needed to maintain a steady level of calcium in the blood. If people do not consume enough calcium , too much calcium is mobilized from the bones, weakening them..

Total Body Water is primarily maintained via extracellular Sodium concentration. Extracellular Sodium is maintained at 135-145 mEq/L; Sodium (Na+) is the … The body maintains the right level of potassium by matching the amount of potassium consumed with the amount lost. Potassium is consumed in food and drinks that contain electrolytes (including potassium) and lost primarily in urine.
Potassium is one of the major electrolytes (together with sodium, chloride and magnesium) that conducts electricity in the human body. It also plays important roles in muscle contraction, nerve impulse transmission, and in maintaining the balance of fluids in the body. • Sodium is an essential nutrient and is needed by the human body in occur). • Sodium is important for many body processes, such as fluid balance, muscle contraction, and nervous system function. • As a food ingredient, sodium has multiple uses, such as for curing meat, baking, thickening, retaining moisture, enhancing flavor (including the flavor of other ingredients), and as a
are sodium, potassium, and chloride, which are lost in sweat along with water. What are the functions of electrolytes? Sodium regulates the total amount of water in the body and maintains the proper function of the nervous, muscular, and other systems. Potassium is responsible for regulating heartbeat and mus-cle function and is important in neuron function. Extreme high or low potassium Sodium performs an important function in the human body.. It is responsible for the blood pressure of our body.. High or low blood pressure can cause unnecessary problems for us.. Sodium also helps the nerves and the muscles to function properly.
of its function include regulating the concentrations of various electrolytes in the body fluids and maintaining normal pH of the blood. Several body organs carry out excretion, but the kidneys are the most important excretory organ. 7/12/2018 · Sodium also works in concert with potassium to maintain normal water balance in the body. Each of the minerals chemically attracts water to itself, thus assuring that optimal levels of hydration are maintained both inside human cells and outside …
Role of Sodium in Human Body The human body contains approximately 1.3 g of sodium. About a third is found in our bones. The rest is our body fluids. It ensures a proper fluid and electrolyte or pH balance in our body, together with chlorine and potassium. Sodium in the form of sodium chloride is ingested directly though food and many food materials contain this material. Sodium helps our body Total Body Water is primarily maintained via extracellular Sodium concentration. Extracellular Sodium is maintained at 135-145 mEq/L; Sodium (Na+) is the …
The effects of sodium in the human body include maintaining electrolyte balance in the bloodstream and the proper working of the nervous and muscular systems. HealthCentral says that sodium is an important determinant of the volume of blood in the body and is an important factor in determining blood Sodium Function in Human Body The primary source of dietary salt is sodium chloride, or salt, more than three-quarters of which comes from processed foods. Although sodium is essential to a number of routine body functions, excessive can have unfavorable impacts, particularly for people who are delicate to sodium.
Sodium and potassium are two important elements that play a vital role in the metabolic processes in the human body. Maintaining the ratio between these two elements is key to good health. Electrolytes are present in the human body, and the balance of the electrolytes in our bodies is essential for normal function of our cells and our organs. Common electrolytes that are measured by doctors with blood testing include sodium, potassium, chloride, and bicarbonate.
The human body has an elaborate system for managing and regulating the amount of key trace metals circulating in blood and stored in cells. Nutrient metals from our diet are incorporated into blood if blood levels are depleted, transported into cells if cellular levels are inadequate, or excreted if blood and cell levels are sufficient or overloaded. When this system fails to function properly Most foods have sodium in them. The most common form is sodium chloride, found in table salt. Your body loses a certain amount of sodium each day through sweat and when you go to the bathroom.
Role of Sodium in Human Body The human body contains approximately 1.3 g of sodium. About a third is found in our bones. The rest is our body fluids. It ensures a proper fluid and electrolyte or pH balance in our body, together with chlorine and potassium. Sodium in the form of sodium chloride is ingested directly though food and many food materials contain this material. Sodium helps our body of its function include regulating the concentrations of various electrolytes in the body fluids and maintaining normal pH of the blood. Several body organs carry out excretion, but the kidneys are the most important excretory organ.
of its function include regulating the concentrations of various electrolytes in the body fluids and maintaining normal pH of the blood. Several body organs carry out excretion, but the kidneys are the most important excretory organ. Sodium plays a key role in normal nerve and muscle function. The body obtains sodium through food and drink and loses it primarily in sweat and urine. Healthy kidneys maintain a consistent level of sodium in the body by adjusting the amount excreted in the urine.

Potassium is a mineral necessary for the proper function of many of your body systems; it's also often referred to as one of the key electrolytes in your body. Potassium, along with sodium, the other electrolyte, plays a vital role in regulating the fluid levels in your body. Potassium has many Electrolytes are present in the human body, and the balance of the electrolytes in our bodies is essential for normal function of our cells and our organs. Common electrolytes that are measured by doctors with blood testing include sodium, potassium, chloride, and bicarbonate.


